Business Lending
Indicted Loan Brokers Out On Bond, 1 Still in Custody
April 5, 2019 Four of the five loan brokers indicted in a fake business loan scam that tricked an Ohio resident out of hundreds of thousands of dollars in upfront fees, have been released on bond. Only one, a defendant by the name of Haki Toplica, remains in custody. All of the defendants have entered pleas of not guilty.
Four of the five loan brokers indicted in a fake business loan scam that tricked an Ohio resident out of hundreds of thousands of dollars in upfront fees, have been released on bond. Only one, a defendant by the name of Haki Toplica, remains in custody. All of the defendants have entered pleas of not guilty.
In addition to the victim being asked for hundreds of thousands of dollars in upfront fees to apply for phony loans, he also signed over the title of 55 vehicles to the defendants to serve as the collateral. The vehicles included a Ford Mustang, several dump trucks, several tractors, several restored classic vehicles, a Freightliner motor home, and trailers.
Toplica was arrested in December and his co-conspirators in March. All of them are New York residents. The condition of one defendant’s release was that she remain working with her present employer. deBanked determined that her most recent employment was ironically that of a business loan broker.
Online Lender Offering “Incredible” Returns to Investors is Recording Massive Losses
March 29, 2019 StreetShares continues to rack up astronomical losses, according to the company’s recently filed unaudited financial statements. The company recorded a $6.4 million loss for the second half of 2018 on only $1.88 million in operating revenue. As in previous periods, payroll continues to be the largest expense.
StreetShares continues to rack up astronomical losses, according to the company’s recently filed unaudited financial statements. The company recorded a $6.4 million loss for the second half of 2018 on only $1.88 million in operating revenue. As in previous periods, payroll continues to be the largest expense.
StreetShares’ funding comes in part from mom & pop investors that are offered a fixed annual return of 5% regardless of how the company’s underlying loans perform. Advertisements on the website call it “incredible” and trumpet that you can “grow your money like a 2x World War champ” and that “your balance will grow every day.” The offering is called a veteran business bond but it has no government backing and can suffer a total risk of loss, all while the underlying loans may not even be made to veteran-owned businesses.
A simple explanation on the site for how it works is that you just open an account, transfer funds from your bank and then just “watch the interest start piling up.” You can withdraw your money anytime but large withdrawals over $50,000 can take up to 30 days to process, the company states. The attractive terms have allowed StreetShares to take in millions of dollars from everyday people with amounts as small as $25.
Institutional investors can earn even higher returns. Lendit Co-founder Peter Renton recently called StreetShares his “top performing investment by a long way,” beating his investments in Lending Club, Prosper, P2Binvestor, Peerstreet, Yieldstreet, Money360, Fundrise, and even the returns previously and erroneously reported by Direct Lending Investments.
deBanked previously reported that on January 1st, Jesse Cushman, the company’s Chief Business Officer and Principal Financial & Accounting Officer, resigned. However, his name continues to remain on the website’s Leadership page a full 3 months later. The company still has not named a permanent successor. deBanked emailed StreetShares earlier in the week about Cushman’s departure and was told that he left to pursue another opportunity. “Steve Vickrey, has been in place since before he left,” President Mickey Konson responded. Konson has been filling in as acting Principal Accounting Officer in the meantime.
In a press release published by StreetShares on Tuesday about a new credit card offering, StreetShares CEO/co-Founder & Iraq War Veteran Mark L. Rockefeller, said, “Veterans love to help other veterans. StreetShares is a veteran-run company, and the goal of the card is not only to provide a veteran focused payments tool, but also to benefit the veteran community as a whole by funding programs that benefit veteran entrepreneurship.”
Tiny Small Businesses Struggle More Than the Rest
March 28, 2019 The average credit score of the owner of a “mom and pop” shop (a business with four or fewer employees) is 30 points lower than the owner of a larger business, according to a recent study conducted by Lendio. (Lendio defined a “mom and pop” business and having four or fewer employees). Furthermore, the study says that, on average, mom and pop businesses require twice as many interactions with a lending expert, compared to larger small businesses. This is likely because of problems with credit and other financial challenges.
The average credit score of the owner of a “mom and pop” shop (a business with four or fewer employees) is 30 points lower than the owner of a larger business, according to a recent study conducted by Lendio. (Lendio defined a “mom and pop” business and having four or fewer employees). Furthermore, the study says that, on average, mom and pop businesses require twice as many interactions with a lending expert, compared to larger small businesses. This is likely because of problems with credit and other financial challenges.
Smaller mom and pop businesses are in greater need of capital, according to the study. These businesses represent 53% of the customers funded through Lendio’s online marketplace. And their loans account for 34% of the total loan volume funded, even though the average size of their loans is smaller. The average loan amount for a “mom and pop” business is less than half that of larger businesses. Specifically, the average loan amount for “mom and pop” businesses is $23,081, while the average loan amount for larger small businesses is $54,188. Of course, a larger company with greater sales can afford to borrow more. But the $54,188 average loan size for larger companies may be a smaller percentage of revenue for those larger companies.
Speaking of revenue, mom and pop businesses’ monthly revenues are on average $35,000 less than their non-mom and pop small business counterparts. The smaller mom and pop shops are also generally younger, according to the Lendio study. Their average time in business is 5.6 years compared to 7.4 years for the larger small businesses.
Undercover in the Underwriting Room
March 22, 2019 Think of the stereotype of a high energy, high testosterone sales floor of men practically shouting on the phone. And then scale it down to a level of about 2 out of 10. That was the environment I stepped into on a recent visit to a room of small business finance underwriters. They let me shadow one for a day so long as I didn’t reveal who they were.
Think of the stereotype of a high energy, high testosterone sales floor of men practically shouting on the phone. And then scale it down to a level of about 2 out of 10. That was the environment I stepped into on a recent visit to a room of small business finance underwriters. They let me shadow one for a day so long as I didn’t reveal who they were.
In the glass room where almost 10 underwriters sat, some spoke on the phone, but the conversations were measured. No shouting. No arguing. Sometimes there was near silence. More than anything, there was an air of focus. After all, when you’re evaluating dozens of documents, just a single oversight can cost the company a lot of money.
“You don’t want to be the guy who loses the company money because you didn’t see a red flag,” said the underwriter.
He asked me to sit beside his desk and watch the funding decisions he was making based on what he saw in the file. He surely didn’t take the merchant’s monthly sales numbers at face value. For instance, in one file, in addition to subtracting a $2,000 transfer from the owner’s personal account into their business account, he also noticed a $4.18 refund from Walmart that was being counted as sales.
“That’s not sales,” he said, and he subtracted $4.18 from the monthly sales number. In one instance, $103,000 in reported sales became $75,000, according to the underwriter.
 While you could certainly feel the concentration in the room, it wasn’t quite a library either.
While you could certainly feel the concentration in the room, it wasn’t quite a library either.
“His FICO sucks,” one of the underwriters said to the others. “His FICO went down and he’s stacked. No.”
When an underwriter is uncertain about a decision, he’ll ask for everyone’s two cents. He said they call these impromptu discussions the “underwriters’ den.”
All the deals we looked at got declined, but I’m told that one underwriter can fund as many as five deals in a day, and then go a few days without funding any.
While the underwriting criteria is taken seriously, sometimes you can be a little more aggressive and push the boundaries a bit if it’s a deal you really like. That takes considerable thought and reasoning. But when the answer is going to be no, it can come at light speed. A few of them happened in under three minutes while I was there. And that was with him slowing down to narrate for me what he was thinking.
“I give a look at [most of] the documents in the file first,” he said, “so that if there’s an obvious red flag, I don’t want to spend time on it.”
In his cursory glance, he’ll look at the business owner’s FICO score, years in business, if the company has other financing, and if so, how they’ve been able to handle those payments. He’ll also count the number of negative days (when the company owes money and has none) and note how consistently the company makes sales.
“Consistency gives me comfort,” he said. “I can give them a stronger offer when they show consistent sales.”
Of course, funding a file takes a good bit longer because you have to continue to vet the business and the business owner, almost as if you suspect there’s something wrong. Has the owner ever been convicted of fraud? Have they owned any other businesses? Did the owner ever default on a loan? It can seem hard for small businesses to pass all these background checks. But the funder has to protect itself and the underwriter’s job is to do just that.
“We’re in the business of giving out money, but within limits.”
LinkedIn Posts Are Turning Into Deals & Dollars
March 14, 2019
 On average, I sign up one ISO every time I post a message on LinkedIn, says Jennie Villano, VP of Business Development at Kalamata Capital Group. They don’t all end up submitting business, she adds, but overall it works. It costs her nothing more than her time and it produces results.
On average, I sign up one ISO every time I post a message on LinkedIn, says Jennie Villano, VP of Business Development at Kalamata Capital Group. They don’t all end up submitting business, she adds, but overall it works. It costs her nothing more than her time and it produces results.
Villano is among the growing crowd of industry insiders attempting to convert social media posts into measurable business. With more than 600 million users on LinkedIn, there is no question about the potential to reach clients. The prevailing wisdom is that you need to be on social media and sharing, but share what exactly?
New Hampshire-based Everlasting Capital is building a window into the business lives of co-founders Josh Feinberg and Will Murphy. One of their recent social media posts focused on their search for a new office lease, while another was a video stream of Feinberg making a real live cold call. The rewards span the gamut, from merchants seeking funding to offers to speak professionally in front of large audiences. And it’s not just about them. “We have worked with our employees to get confident on camera which is making them a lot more comfortable on the phone,” Feinberg said.
 Anthony Collin, CEO of New York-based Smart Business Funding, also attests to LinkedIn. “We definitely generate sales from posting online,” Collin shared, explaining that it was a mix of ISOs and merchants who reach out. Collin said that he and two others in the company meet weekly to generate ideas for the daily posts. They try to make the posts timely, either related to something going on in the industry or to current events, like national elections.
Anthony Collin, CEO of New York-based Smart Business Funding, also attests to LinkedIn. “We definitely generate sales from posting online,” Collin shared, explaining that it was a mix of ISOs and merchants who reach out. Collin said that he and two others in the company meet weekly to generate ideas for the daily posts. They try to make the posts timely, either related to something going on in the industry or to current events, like national elections.
For Jennie Villano, it’s not always a sales pitch. She has posted about being a single mom and about how to keep an upbeat attitude. “Your co-workers, your friends. Are they positive, or are they always complaining?” Villano asks in the video. “Try to surround yourself with positive people who see the best in everything.” She’ll typically extend the offer to do business in the videos that she makes and shares, but not all of them. She shares 2-3 videos a week and her posts typically receive thousands of views.
 Sometimes a video needs a little bit of priming to draw the viewer in. Everlasting Capital, for example, filmed an executive making a sales pitch in their conference room to company CEO Josh Feinberg. But it’s something you must watch, or so the title of the post suggests, because they say the executive drove 10 hours to the office for the opportunity.
Sometimes a video needs a little bit of priming to draw the viewer in. Everlasting Capital, for example, filmed an executive making a sales pitch in their conference room to company CEO Josh Feinberg. But it’s something you must watch, or so the title of the post suggests, because they say the executive drove 10 hours to the office for the opportunity.
Though other social networks are being used in full force by many industry players, LinkedIn is definitely a platform to consider. “We’ve gotten tremendous value from posting to LinkedIn,” Smart Business Funding’s Collin said.
Competition Steps Up in Canadian Small Business Lending Market
March 11, 2019 Last week’s announcement by Funding Circle that it will establish an operation in Canada later this year is part of a trend of large non-Canadian funders entering or expanding into the Canadian market, according to Adam Benaroch, President of CanaCap, a small business funder based in Montreal.
Last week’s announcement by Funding Circle that it will establish an operation in Canada later this year is part of a trend of large non-Canadian funders entering or expanding into the Canadian market, according to Adam Benaroch, President of CanaCap, a small business funder based in Montreal.
Funding Circle started in the UK and expanded outwards to the US, Germany, and The Netherlands, but the UK still comprises of more than 60% of their global origination volume. Their foray into Canada is a good thing for small business owners and lenders, according to Paul Pitcher, founder and CEO of SharpShooter, a funder based in Toronto.
“I see it as win-win,” Pitcher said.
He said that a win for Canadian small business owners is a win for SharpShooter because it means more potential merchant clients. Pitcher said that he loves OnDeck, a rival, is in Canada, in part because OnDeck’s marketing has helped educate Canadian merchants about alternative lending products.
Similarly, Benaroch said he thinks that big companies entering the Canadian market will affect CanaCap positively. For instance, Benaroch said that CanaCap hopes to capture companies that get turned down from OnDeck. And perhaps CanaCap can also capture merchants that are declined by Funding Circle.
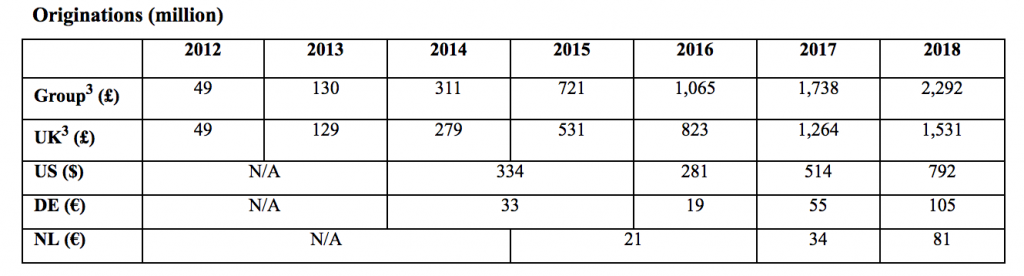 Funding Circle’s loan originations by country by year
Funding Circle’s loan originations by country by year
Benaroch noted that not all outside funding companies have succeeded in Canada, often because they never established a physical presence there. But Funding Circle will be opening a physical office in Toronto.
“We have been evaluating options for expansion over the last year,” said Tom Eilon, who will be Managing Director of Funding Circle Canada. “Canada’s stable, growing economy coupled with good access to credit data and a progressive regulatory environment, made it the obvious choice. The most important factor [in coming to Canada] though was the clear need for additional funding options among Canadian SMEs.”
Funding Circle’s announcement comes on the heels of OnDeck’s December 2018 acquisition of Evolocity Financial Group, a small business funder based in Montreal. While OnDeck started operating in Canada as early as 2015, CanaCap’s Adam Benaroch said that the acquisition of Evolocity is a significant step for OnDeck because Evolocity has an ISO channel in Canada. That runs counter to Funding Circle’s model of mainly going direct to merchant, at least in the US.
Square Capital On Pace to Overtake OnDeck in Small Business Lending
February 28, 2019 OnDeck’s annual loan origination volume has more than doubled since 2014, from $1.2 billion to $2.5 billion, allowing them to retain the top spot in deBanked’s small business funder rankings. But Square Capital, the small business lending division of Square, has grown by 16x since 2014. In the course of 5 years, they’ve gone from being a footnote compared to OnDeck to a fierce rival that is rapidly closing the gap in loan volume.
OnDeck’s annual loan origination volume has more than doubled since 2014, from $1.2 billion to $2.5 billion, allowing them to retain the top spot in deBanked’s small business funder rankings. But Square Capital, the small business lending division of Square, has grown by 16x since 2014. In the course of 5 years, they’ve gone from being a footnote compared to OnDeck to a fierce rival that is rapidly closing the gap in loan volume.
Square’s secret is the ability to generate loan volume at virtually no cost because the product is merely an add-on to their payments-first business. And that’s a problem for OnDeck, because Square has a lot of money to spend on marketing its payments business. More than $400 million a year to be precise. OnDeck, meanwhile, only spent $44 million last year on sales and marketing.
With OnDeck being outspent by a factor of 10, there is a likelihood that Square will overtake OnDeck in the business loan market within the next two years.
And Square’s strength is the ecosystem it’s building. On the Q4 earnings call, company CEO Jack Dorsey said, “I believe the ecosystem is extremely sticky, because it builds durable relationships. If we’re just focused on providing payments in the Register, certainly, there are so many other competitors out there. But when people come in for payments in the Register and then they use [our] payroll for their restaurant and they use Caviar and are really getting offers from Square Capital, it’s really hard to find that mix anywhere else and that builds durability.”
The Art of Moving The Deal – When it becomes too high risk for you
February 27, 2019 OakNorth, a small and medium sized business lender and online bank, has mastered a strategy to avoid merchants from defaulting 100% of the time, according to a story published in Quartz. The strategy: tell the merchants at risk of defaulting to refinance their loans at a competitor.
OakNorth, a small and medium sized business lender and online bank, has mastered a strategy to avoid merchants from defaulting 100% of the time, according to a story published in Quartz. The strategy: tell the merchants at risk of defaulting to refinance their loans at a competitor.
“We’ve said [to merchants], ‘Go renegotiate with another bank and refinance,’” OakNorth co-founder Joel Perlman said at the Finovate Europe conference in London on February 14, according to the Quartz story. “And they’ve gone and refinanced and then a few months later they’ve gone into default.”
Perlman’s phrasing may sound a little harsh, but the practice of moving at-risk merchants to another funder is really not uncommon. In fact, it seems like a fairly common and well-understood concept.
CEO of Accord Business Funding Adam Beebe said that brokers will contact Accord when their merchant is up for renewal. And if Accord knows it can’t continue to fund the merchant – either because it has missed payments or because it has become overburdened with other debt – the broker will shop that undesirable merchant elsewhere.
The merchant goes to a new funder and Accord is pleased to be rid of the merchant and not have it default on Accord’s balance sheet. Beebe notes, however, that the new funder is made aware of the merchant’s financial situation and is able to handle the higher risk. Transparency, he says, is important, particularly in a scenario like this.
Similarly, Heather Francis, CEO of Elevate Funding, said that she is more than happy for an ISO to move a stacking and defaulting merchant away from Elevate, as long as Elevate gets paid. Elevate only funds first position and Francis said they make it very clear to merchants that stacking (taking on additional funding from other sources before satisfying an existing contract) is not allowed.
“If a merchant is stacking, that’s not someone we want to work with,” Francis said. “And if the [new] funder understands the high risk, then is fine.”
As long as nothing is being hidden from the new funder, then it seems this practice is just an element of how funding works.
From the broker side, Rob Addison, Managing Member of Sentra Funding, an ISO, said that when a funder knows it will not be renewing one of his merchants, they will ask him to take the merchant away.
Addison said that some funders are so eager to get rid of defaulting merchants that they will offer deals like reducing the merchant’s balance just to get the merchant away from them.
It may not sound nice to jettison a defaulting merchant, but if a funder can avoid a merchant defaulting on its dime, then in many cases, it will.
“We try to move a financially distressed merchant from from, say, an MCA to a longer term loan,” Addison said. “If they haven’t been stacked, they have options. If they have, it’s harder. But if they have something, like commercial property or equipment, there’s usually a [a funder] willing to step in.”





























