Business Lending
deBanked CONNECT MIAMI 2020 Photos
January 21, 2020View a selection of deBanked CONNECT MIAMI photos here
View every official deBanked CONNECT MIAMI 2020 photo on facebook
Ready for deBanked’s biggest event of the year? Broker Fair returns to New York City on May 18th
Declined For Funding? Lack of Time in Business Beats Out Lack of Credit Worthiness
January 20, 2020 A study conducted by Square Capital and the Stevens Center for Innovation in Finance at the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania, pulled back the curtain on small businesses and the financing process.
A study conducted by Square Capital and the Stevens Center for Innovation in Finance at the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania, pulled back the curtain on small businesses and the financing process.
Notably, the #1 reason that businesses said they had been declined for funding (regardless of the source) wasn’t credit, it was that they hadn’t been in business long enough.
#2 was (ironically) a lack of cash in the bank.
#3 was insufficient collateral.
Personal credit worthiness and business credit worthiness ranked #4 and #6 respectively.
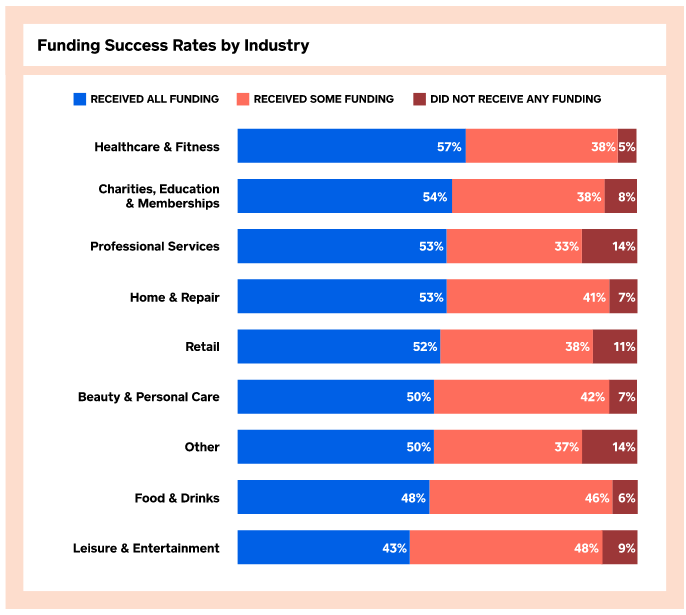
These findings were one of many in the report published by Square last week. Among other key details were that healthcare & fitness businesses were the most likely to receive all the funding they sought whereas leisure & entertainment businesses were the least likely to receive all the funding they sought.
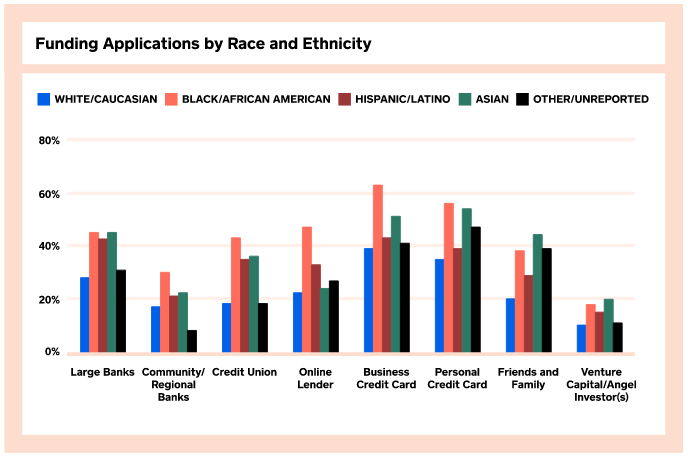
Black/African American business owners were more likely to apply for financing in the last 12 months than any other ethnic/racial group. A chart in the report shows that they were more than twice as likely to apply to an online lender or credit union than white business owners.
Nav Co-founders Step Down From C-Level Positions
January 14, 2020 Levi King, a co-founder of Nav Inc., resigned as the company’s CEO on Tuesday. In a two-part explanation on LinkedIn, King wrote. “To be clear, I’m not burned out on Nav. I’m not aspiring to do something elsewhere, and I’m not leaving the company. I’m still dedicated and passionate about helping Nav succeed. And, I will – just in a different capacity moving forward.”
Levi King, a co-founder of Nav Inc., resigned as the company’s CEO on Tuesday. In a two-part explanation on LinkedIn, King wrote. “To be clear, I’m not burned out on Nav. I’m not aspiring to do something elsewhere, and I’m not leaving the company. I’m still dedicated and passionate about helping Nav succeed. And, I will – just in a different capacity moving forward.”
King will do that by serving as the executive chairman of the board of directors. President & COO Greg Ott will take over as CEO.
On LinkedIn, King further wrote that the company needs “a more qualified leader” to take Nav to the next level after he and co-founder Caton Hanson have successfully grown the company to the right point.
Hanson, who served as the company’s Chief Legal & Compliance Officer, also stepped down and updated his job role with Nav to that of being “Of Counsel” on a part-time basis. Unlike King’s message on LinkedIn, Hanson’s reads as a farewell.
“Thank you for believing in me and our dream,” he wrote. “Thank you for your part in helping Nav achieve what some have called ‘impossible’. I am grateful to know you, have had the opportunity to work alongside you and to call you friends (and for many of you — co-owners). I look forward to Nav’s next chapter – and mine.”
Greg Ott, the new leader of the company, is said in a Nav press announcement to have served as a strategic and organizational leader in both startups and Fortune 1000 corporations. Prior to joining Nav, Ott served as Vice President of Marketing for Intuit QuickBooks.
“Nav’s founders created a company that is truly unique in its ability to revolutionize how small business owners navigate and access capital to grow their business,” Ott commented. “I look forward to building upon Nav’s successes and furthering the company’s vision of aligning financing qualifications, predicting needs, and facilitating transactions between data providers, lenders, partners and small businesses.”
New Jersey Firms Up Its Confession of Judgment Bill
January 13, 2020The New Jersey State legislature strengthened its Confession of Judgment (COJ) bill last week by adding language that grants the Attorney General power to enforce monetary penalties against violators.
S3581 would prohibit any provider of business financing from extending financing with a COJ. Business financing is defined as a loan, line of credit, cash advance, factoring, or asset-based transaction for a business purpose.
The bill still needs to pass the Senate and Assembly and be signed off by the Governor in order to become law. The bill’s sponsor, Senator Troy Singleton, is a Democrat, increasing the likelihood that the Democrat-controlled legislature and Democrat Governor Phil Murphy will move it forward.
Dodd-Frank’s Small Business Lending Data Collection Rule Could Still Take Years to Implement
January 12, 2020 Small business lenders: Are you ready to regularly submit loan application data to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau? No? Good, because almost ten years after Dodd-Frank passed, the provision that requires the CFPB to collect small business lending data still hasn’t been implemented.
Small business lenders: Are you ready to regularly submit loan application data to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau? No? Good, because almost ten years after Dodd-Frank passed, the provision that requires the CFPB to collect small business lending data still hasn’t been implemented.
And apparently we’re still years away.
Section 1071, as it’s known, modified the Equal Credit Opportunity Act and defined a small business lender as any company that engages in any financial activity. So if you’re wondering if this thing even applies to whatever you do in your corner of small business finance, it probably does.
The rule has taken so long to implement that consumer advocacy groups have actually sued the CFPB over the delay. The CFPB took note followed by initiative and hosted a symposium late last year to discuss how it might go forward. The next steps from here are to convene a panel of small business lenders, have that panel issue a report, propose what the rules on collection will be, collect feedback on the proposal, formulate a final rule, issue a rule, and then set a time for when it will go into effect. That process could mean that the earliest that data collection takes place is in 2023, possibly even longer as the entire financial services industry may need time to develop the infrastructure and human resources to comply.
Beyond that, advocates and critics of Section 1071 do not even entirely agree on what purpose data collection will even serve. Some believe the intent is merely for the government to have access to data it otherwise might not have while others believe that the CFPB could use statistics it deems discriminatory to bring enforcement actions against financial institutions. Sounds like we could use a few more years to get on the same page…
A recording of the 2019 Symposium is below:
New Small Business Administration Chief Confirmed
January 9, 2020The newest Administrator of the SBA was announced on Tuesday. Jovita Carranza was appointed after President Trump had tweeted the previous Thursday about her nomination.
I am pleased to announce that Jovita Carranza will be nominated as the new @SBAgov Administrator. She will be replacing Linda McMahon, who has done an outstanding job. Jovita was a great Treasurer of the United States – and I look forward to her joining my Cabinet!
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) April 5, 2019
Replacing Linda McMahon, of WWE corporate fame who left the position in early 2019 to work at pro-Trump super PAC America First Action, Carranza will be the SBA’s first permanent leader in just under a year. The Administration had been led by Chris Pilkerton as the Acting Administrator in the interim.
 Nominated by bipartisan vote of 88-5 in the Senate, Carranza appears to draw support from both sides of the political spectrum. Among those who voted against Carranza were former Democratic presidential nominee hopefuls Kamala Harris and Kirsten Gillibrand. Speaking on the appointment, Democrat and Ranking Member of the Senate Committee on Small Business and Entrepreneurship Ben Cardin said that he was “optimistic that Treasurer Carranza can be the leader and advocate that the Small Business Administration and American small businesses need right now.”
Nominated by bipartisan vote of 88-5 in the Senate, Carranza appears to draw support from both sides of the political spectrum. Among those who voted against Carranza were former Democratic presidential nominee hopefuls Kamala Harris and Kirsten Gillibrand. Speaking on the appointment, Democrat and Ranking Member of the Senate Committee on Small Business and Entrepreneurship Ben Cardin said that he was “optimistic that Treasurer Carranza can be the leader and advocate that the Small Business Administration and American small businesses need right now.”
Discussing her confirmation, a moment of political unity in an increasingly divided period for Washington, Heidi Chung of Yahoo! Finance noted the duality that Carranza brings to the office: “Long been known as someone for the people, she want to definitely help women as well as people of color, so I think, broadly speaking, even though she is a Trump favorite, I think a lot of people are looking forward to what she’s going to bring to the table when she really takes this job on.”
Having served as United States Treasurer from 2017 to 2019, Carranza was responsible for the operations of the US Mint, had dealings with the Federal Reserve, acted as an advisor to Secretary of the Treasury Stephen Mnuchin, and is likely to appear inside your wallet as a signature on dollar bills. Carranza also served as Deputy Administrator in the SBA during George W. Bush’s presidency.
Prior to her time in Washington however, Carranza worked at UPS for over twenty years. Starting off as a part-time truck loader, Carranza worked her way up through the package delivery service to become President of the company’s Latin American and Caribbean operations and subsequently Vice President of Air Operations from their Louisville, Kentucky facility.
Having worked at UPS while being a young mother and attending college, Carranza said on those years that “I thought if I could make it out of this situation – having an opportunity to acquire leadership and managerial skills; receiving on-the-job training – I would be able to finance higher education for myself; secure better caretakers and schools for my daughter – this is the American dream – what I strived to achieve not looking back!”
Carranza was born in Chicago to Mexican immigrant parents. Her father working as a factory foreman and her mother as a housewife. According to Carranza, her mother read a newspaper every day in order to teach herself English.
Seen as a long-time ally to Mnuchin, Carranza is credited by the Secretary as being instrumental in Republicans’ 2017 tax bill, and has said in a statement that she will “continue to promote pro-growth economic policies, eliminate job-killing regulations, and fight for the small businesses that are the lifeblood of the American economy.”
When asked at her Senate confirmation hearing in December what she would do in office, Carranza said that she would “put particular emphasis on opening more doors for women and for entrepreneurs in underserved communities, including military families and veterans,” and that she “will be a tireless advocate in the Cabinet for small businesses.”
Created in 1953, Carranza will be the SBA’s 44th Administrator, working with a budget of $820 million for 2020.
Big Money, Small Town: How SBA Loans Are Powering America
December 26, 2019
 “The Mountains Are Calling” is the motto of Gatlinburg, an East Tennessee town of roughly 4,000 citizens known for its spectacular views of the Smoky Mountains and as a jumping-off spot for hikers, campers and winter skiers. The town also offers attractions such as Ripley’s Aquarium and arts-and-crafts festivals.
“The Mountains Are Calling” is the motto of Gatlinburg, an East Tennessee town of roughly 4,000 citizens known for its spectacular views of the Smoky Mountains and as a jumping-off spot for hikers, campers and winter skiers. The town also offers attractions such as Ripley’s Aquarium and arts-and-crafts festivals.
To get around, 800,000 tourists and locals alike hop aboard the 20-odd trolley buses operated by Gatlinburg Trolley, the private transit system. Few riders marveling at the picturesque scenery and enjoying the sprightly vehicles, which recall San Francisco’s cable cars, know that they’re riding a custom-made trolley-bus built by Hometown Trolley of Crandon, Wisconsin.
 And even fewer would know that the chief executive and president of that company is Kristina Pence-Dunow, making it the only female-owned manufacturer of transit vehicles in the US. Bolstering the manufacturing enterprise—which Pence-Dunow acquired in 1997 from her ex-husband, who wanted to “liquidate” it, she says—have been multiple bank loans backed by the Small Business Administration.
And even fewer would know that the chief executive and president of that company is Kristina Pence-Dunow, making it the only female-owned manufacturer of transit vehicles in the US. Bolstering the manufacturing enterprise—which Pence-Dunow acquired in 1997 from her ex-husband, who wanted to “liquidate” it, she says—have been multiple bank loans backed by the Small Business Administration.
The most crucial SBA loan came in 2005, she says, just as she was nearly driven out of business in a price war. “We had to be innovative” to survive the cutthroat competition, Pence-Dunow told deBanked in a telephone interview.
Using a $350,000, five-year SBA credit issued by River Valley Bank (now Incredible Bank of Wausau, Wis.), the transit company developed the prototype for a “lowfloor entry vehicle.” The design feature made her trolleys accessible to riders with walkers and wheelchairs and enabled the company to beat out its competitor for a key contract with Hampton Roads (Va.) Transit. That deal, in turn, generated sales to transit authorities in Miami Beach, Laguna Beach, and the University of Oklahoma.
Subsequent SBA loans, Pence-Dunow says, enabled the company to create its own dealer network and develop battery-powered, clean-energy vehicles. The financings also allowed her to buy out, in 2016, the rival trolley company that had tried to run her buses off the road.
Her grit and determination—for many years Pence-Dunow ran the company as a single mother raising two children—have also paid dividends for her Wisconsin community. With annual sales of $20 million and 65 employees receiving health and life insurance as well as pension benefits, Hometown Trolley has brought good-paying jobs to successive generations of families in the Northwoods.
In 2018, she earned the SBA’s “Small Business Person of the Year” award for the state of Wisconsin.
Hometown Trolley, meanwhile, is just one of 30 million small businesses that make up the backbone of the US economy. Small businesses—a small business is broadly defined as a commercial or professional enterprise with fewer than 500 employees—accounted for the employment of 58.9 million people in 2015, according to the US Census Bureau’s most recent figures. That’s just shy of 50% of the country’s total workforce. And it seems that the smaller the better: In 2018, firms employing fewer than 20 employees added 1.1 million net jobs to the US economy, the largest gains among the small business cohort.
 By contrast, large manufacturing companies only employ about 11% of the total workforce, notes Karen G. Mills, former SBA administrator and member of President Barack Obama’s cabinet. The bottom line is that the contribution to the economy made by both small business and the SBA “is under-appreciated,” says Mills, now a senior fellow at Harvard Business School and author of Fintech, Small Business & the American Dream. “It’s a much more powerful job-creator than the manufacturing component of the US economy,” she adds.
By contrast, large manufacturing companies only employ about 11% of the total workforce, notes Karen G. Mills, former SBA administrator and member of President Barack Obama’s cabinet. The bottom line is that the contribution to the economy made by both small business and the SBA “is under-appreciated,” says Mills, now a senior fellow at Harvard Business School and author of Fintech, Small Business & the American Dream. “It’s a much more powerful job-creator than the manufacturing component of the US economy,” she adds.
During the Great Recession, which coincided with her tenure at the SBA, Mills reports that 60% of the country’s job losses were in the small business sector. As many as 1.8 million jobs disappeared in a single quarter in 2009. Mills credits the SBA’s lending as playing a key role in buffering the US economy against even more severe ravages.
To help reverse the economic free-fall, the SBA eliminated all SBA fees and temporarily upped the 75% government credit guarantee to 90%. The agency also persuaded a thousand commercial banks that had not issued an SBA-backed credit since 2000 to turn on the spigots. “Banks are the primary source of financing for small businesses,” she notes. “They (small businesses) can’t go to the credit markets like big business does.”
S.R. Rosati, Inc., an Italian ice manufacturer based in Clifton Heights, Pa., is one of those small businesses that nearly went belly-up. Headed by Richard Trotter, a West Point graduate, former US Army captain and company president, the Italian ice business is thriving today. It has just under 30 employees and reports annual sales of $10 million. But ten years ago it was in desperate straits. “Even though we’re a 100-year-old company,” Trotter says, “we could have been like a ton of businesses that went out of business every week. The SBA helped us get through tough economic times in 2007-2008 when a lot of businesses took a hit.”
The SBA’s flagship product is the 7(a) loan, which range up to $5 million. Almost 2,000 US banks, as well as a number of nonbanks, participate in the program. The loans are currently backed by a 75% government guarantee and are targeted to those entrepreneurs who, the SBA states, “otherwise would not have access to capital to start, grow, or expand their small businesses.”
An SBA loan, former Administrator Mills explains, “is designed to fill a market gap— to make loans to creditworthy borrowers that the market feels are too risky to make without some support.”
Currently bearing an interest rate of 7.75%-9%, according to financial technology firm Fundera, 7(a) loans are affordable and the terms are fairly generous: typically, the borrower has 10 years to repay the loan. The loans can be used for multiple purposes: as working capital, to purchase equipment and inventory, make a business acquisition, meet payroll, hire new employees, and (in some cases) refinance crushing debt.
If a borrower is eligible and able to secure a 7(a) loan, “it’s the gold standard,” remarks Levi King, chief executive and co-founder of Utah-based Nav, an online, credit-data aggregator and financial matchmaker for small businesses.
William McSweeney, chief operating officer in the business banking section at Citizens Bank in Boston, says that insufficient collateral is most often the reason that a small business fails to qualify for a conventional business loan. With an SBA loan, he says, the government guarantee serves as a bulwark “to cover the weakness of a collateral position.”
 He cites the case of a dentist who’s attempting to acquire an existing dental practice for $1 million. Unless the practice owns a building, McSweeney says, there’s probably not enough collateral to support a $1 million borrowing. Yet the deal is attractive: Dentistry is a reliable industry (or “vertical” in lender jargon), the targeted practice has a solid client base, there’s strong cashflow, and the practice boasts a fully equipped armamentarium. “An SBA loan will guarantee the $1 million loan for 75 percent,” McSweeney says. “Now I can ask, ‘Is there $250,000 in collateral.’ That’s the way I look at it.”
He cites the case of a dentist who’s attempting to acquire an existing dental practice for $1 million. Unless the practice owns a building, McSweeney says, there’s probably not enough collateral to support a $1 million borrowing. Yet the deal is attractive: Dentistry is a reliable industry (or “vertical” in lender jargon), the targeted practice has a solid client base, there’s strong cashflow, and the practice boasts a fully equipped armamentarium. “An SBA loan will guarantee the $1 million loan for 75 percent,” McSweeney says. “Now I can ask, ‘Is there $250,000 in collateral.’ That’s the way I look at it.”
Adds Kirk Jacobson, an SBA lender at Northwest Bank branch in Independence, Ohio: “In my experience, the preponderance of SBA loans have a collateral shortfall. Even lending to hotels or something tangible can be risky. The collateral (the hotel) can lose value quickly. The challenge for banks like ours is to use the SBA as the tool where conventional lending doesn’t work.”
By at least one yardstick SBA lending appears to be at a crossroads. The SBA reports that the number of small businesses taking advantage of the 7(a) program fell by 13% in the most recent fiscal year, which ended September 30, 2019. The 52,000 small businesses securing 7(a) credits in 2019 was more than 8,000 fewer than the previous year. The dollar amount of credits acquired also dropped; the $23.7 billion in lending was a 6.5% drop.
This is being taken as a good sign by the agency. “A strong economy is powering America’s 30 million small businesses, and the SBA’s numbers bear that out,” Chris Pilkerton SBA’s acting administrator and general counsel, said in a recent statement. “When the economy is doing well, 7(a) lenders are more willing to provide capital without the need for a federal loan guarantee.”
But even small businesses that are outwardly healthy and experiencing growth often face hardship. Consider the case of Kyle McClelland, owner of Have Lights Will Travel, a Reno-based contractor that handles illumination for office buildings, stores, parking lots, and warehouses across northern Nevada. He got in over his head this year when he subcontracted lighting work for Macy’s and Target parking lots in a string of northern California cities.
There was no money advanced by the main contractor for materials, wages or expenses, he says. As a subcontractor, McClelland doesn’t get paid until the job is done. Yet, almost overnight, he doubled his workforce to 70 employees, footed the bill for a platoon of workers to lighting equipment, all of which exhausted his $100,000 line of credit with a Reno bank. His situation looked dire and it was taking an emotional toll. “The company was on life support.” he says. ”I realized that I needed extra funds to make payroll. I honestly didn’t sleep for months. I was lucky to get three hours of sleep a night.”
McClelland was bailed out in August when he secured a $350,000 line of credit through an SBA Express loan fronted by Five Star Bank, a Sacramento financial institution. SBA Express loans, which are part of the 7(a) program but carry only a 50% government guarantee, can be made in as few as 36 hours. But McClelland says that it took him four weeks to obtain the loan.
Trotter, the owner of the Italian ice company, says that his business too is in an expansion phase and that its financial situation was cramped. He had been saddled with a pricey, short-term note for $1.4 million that was weighing down business. With the intercession of Multifunding, a Philadelphia-area broker, Trotter took out a $2.5 million, 10-year loan with Celtic Bank in Utah at prime plus 2.75%, his third SBA loan in 20 years. The refinancing, which closed in late July, is saving him $30,000 in monthly cashflow, he says, more than $100,000 to date.
“Now we can play a little bit of offense,” he says. “We have the up-front money to go into convenience stores and supermarkets with our product.”
One common experience of the business-people who spoke to deBanked is that assembling the required documents and applying for SBA loans can be a daunting and often discouraging task. “The whole thing with these loans is making sure the I’s are dotted and the T’s are crossed,” says Domenic Rinaldi, managing partner at Sun Acquisitions, a Chicago-based firm specializing in lower middle-market, merger-and-acquisition deals using SBA loans. “The government is demanding,” he adds, “and if everything is not in order, you won’t get your money.”
To cut through the inordinate amount of red tape, many businesses turn to brokers like Multifunding and other financial midwives, who receive a commission from the bank. “The fastest I’ve done an SBA loan is two weeks and the longest is 18 months,” says Ami Kassar, founder and chief executive of Multifunding. He says that the firm’s SBA credit business constitutes 70% of his work and that he relies on a network of 10 banks. “The average time it takes for an SBA loan is probably 90 days,” he adds.
“Grueling” is how Daniel Shemtob of Los Angeles describes his experience obtaining an SBA loan. “I had gone to 30 banks,” he says, “and I did qualify for a loan but I didn’t like the deal.”
Shemtob is the chief executive and—thanks to securing an SBA backed financing for an acquisition—the sole owner of The Lime Truck, which has bragging rights to winning the Food Network’s “Great Truck Race.”
In addition to the truck, his Southern California business also includes a couple of brick-and-mortar restaurants and a catering company. The operation, which will do $5.5 million in sales this year, employs 40 full-time workers plus part-time catering help.
Shemtob finally scored an SBA loan with assistance from Kassar’s Multifunding, which he found through Entrepreneurs’ Organization, where he’s a board member of the L.A. chapter. He was able to take out a pair of 10-year loans totaling $1.8 million with IncredibleBank at prime plus 2.75%. Even with a broker, he says, it took him three months to get the loan, which closed earlier this year. “The ten-year loans give you stability and an affordable payment,” he says. “If I hit my sales targets,” he adds, “the loans will allow me to grow the business.”
But what if he hadn’t obtained SBA-backed financing? “I don’t know if the company would be around today,” Shemtob says.
SBA loans used for acquisitions play a major role in extending the life of enterprises that likely would have disappeared upon the retirement or death of an entrepreneur, the unwillingness of succeeding generations to take control of a family business, or the break-up of a partnership, notes Rinaldi, the Chicago M&A specialist.
To arrange SBA acquisition loans for purchasers of small businesses, Rinaldi deals mainly with 18 banks, including Busey Bank (Champaign, Ill.), U.S. Bancorp (Minneapolis), Byline Bank (Chicago) and Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (Toronto). “Banks may say, ‘Bring us all your manufacturing deals’ and two years later there’s a management change and they’ll only make loans to distribution and service companies,” Rinaldi says. “Part of my job is understanding which sectors are handled by which banks.”
 Meanwhile, an emerging debate is brewing within banking circles about the best use of SBA 7(a) loans, which were capped at $28 billion in the last fiscal year. While the overall U.S. economy has continued to prosper since the Great Recession, and the official unemployment rate has dipped below 4%, the lowest in 50 years, the bounty is being shared unevenly. While most large US cities and suburbs are generally adding jobs and experiencing good times, many rural areas and Rust Belt communities are dealing with stagnant wages, job losses and population outflows.
Meanwhile, an emerging debate is brewing within banking circles about the best use of SBA 7(a) loans, which were capped at $28 billion in the last fiscal year. While the overall U.S. economy has continued to prosper since the Great Recession, and the official unemployment rate has dipped below 4%, the lowest in 50 years, the bounty is being shared unevenly. While most large US cities and suburbs are generally adding jobs and experiencing good times, many rural areas and Rust Belt communities are dealing with stagnant wages, job losses and population outflows.
The question is: Should more banking resources be directed to distressed communities through SBA loans? Or should the banking industry lend as it sees fit, largely focused on profitability and shareholder value, albeit within the SBA’s guidelines, perhaps with a nod to businesses owned by women, minorities and veterans? Many banks incorporate both philosophies. But this dichotomy in operational goals can sometimes be seen in sharp relief.
The stark difference in SBA lending practices between Live Oak Bank of Wilmington, N.C. and Northwest Bank of Warren, Pa. is a case in point.
With $4.6 billion in assets, Live Oak Banking Company, which was founded in 2007, is just a dozen years old but it’s already become the No. 1 SBA lender in the US. In the most recent fiscal year, from just one branch on North Carolina’s seacoast, it made 913 SBA loans totaling $1.347 billion, an average of nearly $1.5 million per loan. To comprehend the magnitude of that accomplishment: Live Oak nearly lapped Wells Fargo Bank, the No. 2 lender with $786.4 million in loan totals, despite the latter’s making triple the number of SBA loans. It also out-lent such worthies as J.P. Morgan Chase and Bank of America, both of which lagged well behind Live Oak in the SBA lending tables.
With its adroit use of technology and its meteoric rise to become an SBA powerhouse, Live Oak has emerged as a Wall Street darling. Thomas Brown, a founder and chief executive at Second Curve Capital, a hedge fund that invests exclusively in financial services companies and manages $150 million in assets, calls Live Oak “a freak of nature.”
“For their veterinarian-lending practice,” Brown observes, “they hire a vet as their lending officer. They do this with all their verticals, whether it’s chicken farming or funeral homes. And when they’re dealing with a client, they have all this incredible expertise.”
Steve Smits, chief credit officer at Live Oak, told deBanked that the bank now lends to 29 verticals across all 50 states. Its most recent additions were early childhood education centers and franchisees for aftermarket companies like Jiffy Lube and Meineke. Not only does Live Oak have experienced loan officers with deep knowledge of their sectors making the loans, but the bank is conscientious about keeping up with its clients. So much so that it maintains a stable of consultants, accountants and other professionals who are on call to add value.
For example, says Smits, a former associate administrator of the SBA’s office of capital access, one of Live Oak’s board members is Jerald Pullins, a former president of Service Corporation International, the Houston-based owner and operator of nearly 1,500 funeral homes and 481 cemeteries in the US and Canada.
For critics who say that an SBA lender should be modeled on George Bailey, the small-town banker immortalized in “It’s a Wonderful Life,” Smits says: “On a moral plane, we visit 100 percent of our small business owners face-to-face at a minimum of a two-year rotation. With 10-year loans, it would be easy to take a hands-off approach, but we’re very vigilant.”
Smits adds: “We’ve had our customers say to us, ‘You know what. You’ve traveled across the country to see me. And I’ve been banking with the branch down the street and they’ve never been in my office.’”
Founded in 1896 and headquartered in Warren, Pa., Northwest Bank’s service area looks like a jagged triangle traversing three states, running from Lancaster, Pa. to greater Cleveland to Buffalo, N.Y. and back. Inside the tri-state perimeter are a plethora of gritty old factory towns and Rust Belt communities.
“Our banks are located in all kinds of small cities,” Jacobson, the bank’s chief SBA lender, says. “I’m biased,” he adds, “but I believe in reinvesting in our communities. Our business model is to lend in our footprint. It’s where our branches are and where our clients are. Our strategy is not to lend around the US.”
One example of Northwest’s targeted SBA lending, Jacobson says, can be seen in Lorain, Ohio, a city of 64,000 on Lake Erie that is working to reinvent itself. Lorain was once the proud home of iconic heavy industries like the American Ship Building Company, a Ford Motor assembly plant, and U.S. Steel’s sprawling mill on the city’s south side. The economy was so dynamic that it “outshined Cleveland” says Kevin Nelson, the Lorain-based president of Northwest Bank’s Ohio region.
 But in the 1980s deindustrialization began to take its toll and the city experienced high unemployment, rising poverty, and urban decay. Now, however, Lorain is hoping to rise like the mythical Phoenix from its ashes. And Northwest Bank is doing its part by marshaling resources in concert with the city’s government, the Black River Port Authority, the Chamber of Commerce, the Lorain Historical Society and other citizens groups to transform the waterfront and downtown into an entertainment center and destination for weddings, rock concerts, and other events.
But in the 1980s deindustrialization began to take its toll and the city experienced high unemployment, rising poverty, and urban decay. Now, however, Lorain is hoping to rise like the mythical Phoenix from its ashes. And Northwest Bank is doing its part by marshaling resources in concert with the city’s government, the Black River Port Authority, the Chamber of Commerce, the Lorain Historical Society and other citizens groups to transform the waterfront and downtown into an entertainment center and destination for weddings, rock concerts, and other events.
Nelson is bullish on the just-completed Broadway Streetscape, in the heart of downtown, which has given Lorain a physical makeover. There are, Nelson says, “new sidewalks, lighting, archways, and parking areas.” Condominiums are being built and the marina is under new management, which could make the city a boating center. Black River Landing has become a magnet for celebrants with more than 200,000 people attending the “Rockin’ on the River” concerts over the summer. And the city is witnessing “new restaurants, coffee shops, bars, and other gathering places for people,” the banker says. “We’re seeing outside investment and we’re just beginning to see Lorain becoming a destination for millennials.”
Many of the trendy new establishments are being financed with SBA loans. “SBA lending has helped us support some of these new ventures coming in,” Nelson says. “They don’t make up for bad credit, lack of a business plan or cashflow,” he adds. “It has to be the right type of business. But SBA loans are a component.”
Who knows? Maybe Lorain will be home to the next Ben & Jerry’s or Calloway Golf, both of which commenced life as small business start-ups. A city can hope, can’t it?
Online Small Business Borrowing Decisions Not Driven By Costs or Disclosures, Fed Study Finds
December 23, 2019 A new study on transparency conducted by the Federal Reserve on non-bank small business finance providers indicates that borrowers are not driven by costs or disclosures. The #1 reason for a business to apply with an online lender was the speed of the process, the study showed. #2 was the likelihood of being funded. Cost ranked near the bottom of the list.
A new study on transparency conducted by the Federal Reserve on non-bank small business finance providers indicates that borrowers are not driven by costs or disclosures. The #1 reason for a business to apply with an online lender was the speed of the process, the study showed. #2 was the likelihood of being funded. Cost ranked near the bottom of the list.
While a focus group pointed out many areas that are ripe for improvement, the Fed was left to conclude that “clearer information—in the form of standardized disclosures—will not necessarily alter the decisions of some small business borrowers about whether and where to obtain financing.”
The Fed further commented that some loan applicants revealed that they had already “committed the expected loan proceeds” before a lender could even present rates and terms. Others borrowers wished they could know their approved rate and terms before even providing a lender with any data. These findings seem to undermine the potential value of enhanced uniformity in disclosures.
The report, which attempts to paint a bleak picture of online lending in spite of the data, seems to validate what online lenders have been saying all along, that speed is supreme. Even where transparency is lacking, it cannot be overstated that big banks scored lower on transparency than online lenders did.
Uncertain Terms: What Small Business Borrowers Find When Browsing Online Lender Websites evaluated BFS Capital, CAN Capital, Credibly, Fundation, Funding Circle, Kabbage, Lending Club, National Funding, OnDeck, Rapid Finance, PayPal Working Capital, and Square Capital.