ACH Advances
Dear Ami
November 19, 2013I don’t know Ami Kassar personally, but I read the articles in his NY Times blog, a column dedicated to chastising merchant cash advance companies. In it he yearns for the glory days of 10 year loans at 8% interest for local mom and pop shops. Having been a broker for 3 years myself, believe me when I say I wish rates were lower and terms were longer. It’d be an easier sell. But having also been a very senior underwriter and risk manager, I know exactly why the terms are what they are.
The below post was intended to be a comment on Ami’s latest post, Assessing a Kevin O’Leary Investment on Shark Tank, but it shattered the 1,500 character limit so I’m posting it here. As it was intended to be a comment and not its own post, I did not expand or delve into as much as I wanted.
—-
 Ami,
Ami,
We get it. You don’t think expensive capital is right or moral and in a perfect world where small businesses have perfect credit and a 0% likelihood of delinquency or default, there probably wouldn’t be a merchant cash advance industry.
Unfortunately, the reality is that many small businesses are high risk borrowers for one reason or another. This isn’t because a bank says so but because there is substantial data that shows there is a high likelihood of delinquency or default. Almost all of the small businesses that existed in my neighborhood 25 years ago are gone. They were replaced by new businesses, which were replaced by new businesses, which were replaced by new businesses. To say that a store with 2 years in business and 700 credit in my neighborhood is a safe long term investment would be a huge mistake. Residents tired of eating the same food, local bars lost their cool factor, the CD store got replaced by digital downloading, the supermarket got replaced by one that only sold organic food, and Blockbuster Video is gone. The Exxon became Shell which turned into Gulf which got torn down and rebuilt as a bank. New extensions to a mall 3 miles away damaged 40+ retail businesses on Main Street. A failed health inspection killed a restaurant, bad Yelp reviews killed the bowling alley, and the 78 year old master tailor didn’t relate to the new generation of residents. A flood closed a clothing store for 2 months, a fire killed a coffee shop, and a hurricane wiped away a strip mall.
Shall I keep going? Partners had a falling out, a son ran his father’s cafe into the ground, development killed a farm stand, and increasing rent put a barbershop over the edge.
I’m not knocking small business, just acknowledging that it’s one of the toughest things in this country to manage. God bless the people that try and especially the ones that last decades.
You know what else happens with a lot of small businesses? They declare losses for tax purposes and make organizing financial documents secondary to all else. To a lender, there is a layer of risk built upon a mountain of risk.
You cited IOU Central as a shining example of rate fairness, but failed to acknowledge that they are wildly unprofitable and have teetered on the brink of insolvency for a year. IOU Central is a publicly traded company and I mean them no disrespect, but check out their books. Lending isn’t supposed to be charity.
SBA loans and defaults are synonymous with each other. It’s great for businesses, but the poor economics of them fall on the taxpayers.
There is this belief that merchant cash advance companies are predatory, but the rates they charge are what the market has priced as sustainable for both parties. There’s more than a hundred funding companies offering the same product. You want to know why the competition hasn’t dropped rates to 10% APR yet? It’s because they’d all be out of business. Rates have come down a little bit, but there is only so far they can drop. Small business is risky business.
As a broker out on the street shaking the wary hands of shop owners, I understand your frustration with the high cost. Believe me, the merchant cash advance companies wish they could lower the prices too. Some have done so at their own peril and closed up shop. Others are on their way to that point now. Would you rather only a tiny fraction of small businesses get non-bank financing at a rate in line with your comfort level and let the rest burn? Small businesses of all credit types and financial standings for years have cried, “HEY, WHAT ABOUT US?!” and in response, private companies made access to capital possible. Often times the money is expensive, very expensive. You are concerned that small business owners are making a mistake when they enter into these agreements yet you admittedly lock them into these deals yourself. It seems as though some of your clients would rather have the opportunity to do something positive with expensive money than have no opportunity at all.
I can think of few things tougher than running a small business. The way my old neighborhood looks today is proof of that. I barely recognize the place. You know what wasn’t around 25 years ago? Merchant cash advance companies. Who knows what would’ve happened if they all had access to capital despite a less than stellar credit rating. Some of those stores may have grew, evolved with the changing times, or become franchises. Things might’ve been different. We all want lower rates, sincerely we do. Competition will drive it down as far as it can go and there’s plenty of that today. Once we hit the floor, if we’re not there already, you will have to ask yourself this question. Are you living in a perfect world or the real one? Let the small businesses decide if the opportunity they’re given is one they want to take.


 I’d like to think that the term, merchant cash advance, is mainstream enough that a congressman would know what it was. I have no idea if that’s the case though. What I do know is that Renaud Laplanche, the CEO of Lending Club gave testimony before the Committee on Small Business of the United States House of Representatives on December 5, 2013.
I’d like to think that the term, merchant cash advance, is mainstream enough that a congressman would know what it was. I have no idea if that’s the case though. What I do know is that Renaud Laplanche, the CEO of Lending Club gave testimony before the Committee on Small Business of the United States House of Representatives on December 5, 2013. Following a wild 18 months of press releases and technology revolutions, I’m hearing that some ISOs are having technology fatigue. VCs and Private Equity want to invest in companies that are automating everything, but that doesn’t necessarily mean account reps are ready for it. The worst fear an account rep has is using an automated system to spit out numbers with a contract, get that contract signed by the merchant, and then have the figures revised or nullified during a later human review. Going back to the merchant with a 2nd contract with new numbers (often times worse) is a major credibility killer for them. It has bait and switch written all over it, even if they’ve made perfectly clear to the merchant that the terms they sign for are subject to a final underwriting review.
Following a wild 18 months of press releases and technology revolutions, I’m hearing that some ISOs are having technology fatigue. VCs and Private Equity want to invest in companies that are automating everything, but that doesn’t necessarily mean account reps are ready for it. The worst fear an account rep has is using an automated system to spit out numbers with a contract, get that contract signed by the merchant, and then have the figures revised or nullified during a later human review. Going back to the merchant with a 2nd contract with new numbers (often times worse) is a major credibility killer for them. It has bait and switch written all over it, even if they’ve made perfectly clear to the merchant that the terms they sign for are subject to a final underwriting review. 




 American Express recently teamed up with Heartland Payment Systems to provide split-processing loans tied to all card transactions rather than just American Express exclusively. The max loan size is $750,000. Prior to this deal American Express and other merchant cash advance companies rarely competed head-to-head. Unless a small business was processing substantial AMEX, they weren’t a candidate for American Express Merchant Financing. I expect them to make similar deals with other card processors.
American Express recently teamed up with Heartland Payment Systems to provide split-processing loans tied to all card transactions rather than just American Express exclusively. The max loan size is $750,000. Prior to this deal American Express and other merchant cash advance companies rarely competed head-to-head. Unless a small business was processing substantial AMEX, they weren’t a candidate for American Express Merchant Financing. I expect them to make similar deals with other card processors. If you missed Friday night’s episode of Shark Tank, you absolutely must catch a rerun of it.
If you missed Friday night’s episode of Shark Tank, you absolutely must catch a rerun of it.  As highlighted in
As highlighted in 







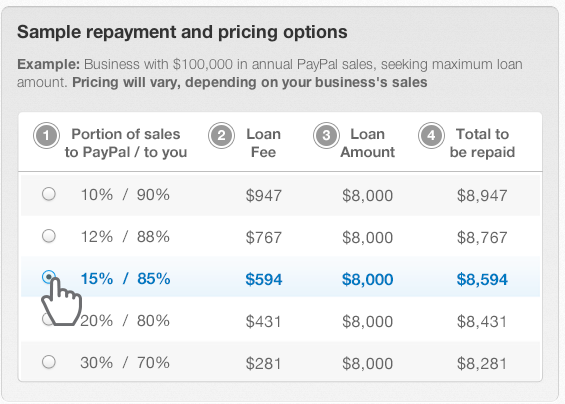
 A few weeks ago, PayPal announced the launch of their Working Capital program as a way to help small businesses in need. They classify it as a loan but the explanation for how it works is textbook merchant cash advance. A percentage of each PayPal sale is withheld and applied as a reduction to the merchant’s balance. PayPal joining the booming merchant cash advance/alternative lending market is really no surprise. After all,
A few weeks ago, PayPal announced the launch of their Working Capital program as a way to help small businesses in need. They classify it as a loan but the explanation for how it works is textbook merchant cash advance. A percentage of each PayPal sale is withheld and applied as a reduction to the merchant’s balance. PayPal joining the booming merchant cash advance/alternative lending market is really no surprise. After all,