Alternative Lending: Big Government and Big Data
– Professor Michael Barr at LendIt 2014
 One of the clear themes of the LendIt 2014 conference was that borrowers are willing to pay extra for speed and convenience. Regulators have taken note of this trend but they’re still supportive of the alternative lending phenomenon anyway. Truth be told, the government is acting like a weight has been lifted off its shoulders. Ever since the 2008 financial crisis, the feds have prodded banks to lend more, but they’ve barely budged, especially with small businesses. Non-bank lenders have relieved them of the stress and all they need do now is make sure everybody plays nice.
One of the clear themes of the LendIt 2014 conference was that borrowers are willing to pay extra for speed and convenience. Regulators have taken note of this trend but they’re still supportive of the alternative lending phenomenon anyway. Truth be told, the government is acting like a weight has been lifted off its shoulders. Ever since the 2008 financial crisis, the feds have prodded banks to lend more, but they’ve barely budged, especially with small businesses. Non-bank lenders have relieved them of the stress and all they need do now is make sure everybody plays nice.
Professor Michael Barr, a former US Treasury official, key architect of the Dodd-Frank Act, and Rhodes Scholar, believes the best way forward is to empower consumers. That’s something lenders can accomplish through education and transparency. On transparency, he cited many of the commendable practices that credit card companies and mortgage companies have implemented, but did not fail to note that these were forcibly instituted through regulation (Hint hint…).
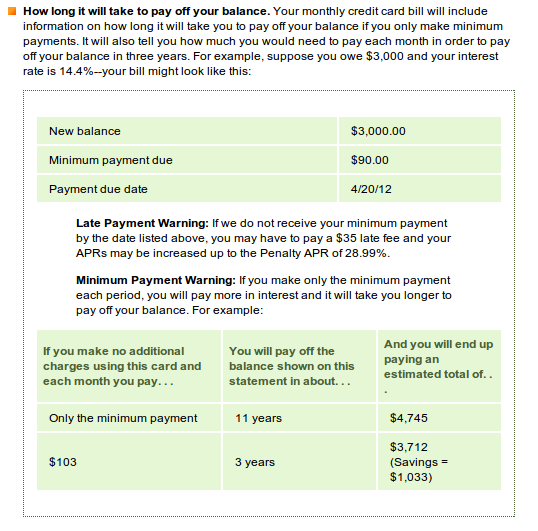
When a LendIt attendee asked Barr to name someone in the alternative lending industry that is a great role model for transparency, Barr answered by saying, “I haven’t seen anyone in the industry doing things the way I would do them in regards to education and disclosure.” On the path towards transparency, “the potential is not yet realized,” he added.
While it sounded as if he favored eventual regulation of alternative lending, he offered all in attendance advice to prevent it. “Take the high road to prevent regulatory interest,” he said.
Barr’s sobering presentation also covered the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) and the role they might play in alternative lending, if any. Payday lenders and debt collectors were their primary supervisory targets he said, but added the “the CFPB has the flexibility in the marketplace to address problems before they occur.” That flexibility essentially gives them jurisdiction over whatever they decide they want to be in their jurisdiction.
Sophie Raseman, the Director of Smart Disclosure in the U.S. Treasury Department’s Office of Consumer Policy appealed to the industry in a different manner. “Small businesses are at the heart of the economy. We want to serve you [alternative lenders] better so that we can better serve them,” Raseman pleaded. As part of that, she came bearing gifts, a reminder that the federal government had loads of data available via APIs at http://finance.data.gov. The government wants to make sure we have access to as many tools as possible, most likely to help drive borrowing costs down. If you need to verify someone’s income, Raseman recommended the IRS’s Income Verification Express Service.
The Income Verification Express Service program is used by mortgage lenders and others within the financial community to confirm the income of a borrower during the processing of a loan application. The IRS provides return transcript, W-2 transcript and 1099 transcript information generally within 2 business days (business day equals 6 a.m. to 2 p.m. local IVES site time) to a third party with the consent of the taxpayer.
The irony with this service is the two business day timeline, though I haven’t confirmed if that’s still the case. Delays and archaic data aggregation methods are the exact things alternative lenders are trying to overcome. Kabbage comes to mind as the length of time it takes for them to go from application to funding can be as quick as 7 minutes, a time frame I found to be reality after watching the demonstration by Kabbage’s COO, Kathryn Petralia.
Kababge’s blazing speed is made possible by access to big data, which made Petralia an excellent choice to have on the Big Data Credit Decisioning Panel. She was joined by Noah Breslow of OnDeck Capital, Jeff Stewart of Lenddo, and Paul Gu of Upstart.
Stewart, whose company lends internationally presented the idea of mining not just data on social networks, but the photographs on them. One possibility was measuring whether or not borrowers appeared in photographs with other borrowers known to be bad, or whether or not they hung out with undesirables such as ex-convicts. He was a big believer in association risk, speculating that friends of bad borrowers also made them more likely to be bad borrowers themselves.
 Breslow of course said you have to be careful with the noise of social media as there can be a lot of false signals. Does that mean there are big data problems then? Upstart’s Paul Gu said, “we have small data problems” in reference to why there seems to be so much trouble evaluating applicants that have little to no credit history. Gu believes that basic information such as where a borrower went to college, their major, and their grades can be used as an accurate predictor of payment performance and his company has acquired the data to back that up.
Breslow of course said you have to be careful with the noise of social media as there can be a lot of false signals. Does that mean there are big data problems then? Upstart’s Paul Gu said, “we have small data problems” in reference to why there seems to be so much trouble evaluating applicants that have little to no credit history. Gu believes that basic information such as where a borrower went to college, their major, and their grades can be used as an accurate predictor of payment performance and his company has acquired the data to back that up.
Somewhere along in the discussion though the meaning of automation got twisted. OnDeck for instance has an automated process, yet humans play a role in 30% of the loan decision making. Does that mean they are not actually automated? Breslow clarified that aggregating data from many different sources using APIs and computers was automation and that there was still a role for humans. The goal is to make sure that humans aren’t doing the same things that the computers are doing.
 “The world’s greatest chess human can beat the world’s greatest chess algorithm,” said Lenddo’s Stewart. “Humans should be pulling what the algorithms can’t think of,” added Breslow. He presented an example of an applicant satisfying all of an algorithm’s criteria but sending up a red flag at the human level. “Why would the owner of a New York restaurant live in California?” Breslow asked. That’s something an algorithm might get confused about. It might mean nothing or it might mean something.
“The world’s greatest chess human can beat the world’s greatest chess algorithm,” said Lenddo’s Stewart. “Humans should be pulling what the algorithms can’t think of,” added Breslow. He presented an example of an applicant satisfying all of an algorithm’s criteria but sending up a red flag at the human level. “Why would the owner of a New York restaurant live in California?” Breslow asked. That’s something an algorithm might get confused about. It might mean nothing or it might mean something.
“Algorithms are probabilistic,” Stewart reminded the audience. They spell out the likelihood of repayment, they don’t guarantee it.
For Kabbage, algorithms and automation have been instrumental in allowing them to scale. “I don’t need to hire a lot more people to serve a lot more customers,” Petralia explained.
“Let the data speak for itself,” Breslow proclaimed. And there is a lot of statistically interesting data. “People with middle names perform better than people without them,” added Breslow.
For Gu, borrowers with degrees in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics fare better than their academic peers, though he wouldn’t reveal which major is #1. That information, while probably available to OnDeck, likely plays little or no role. “There is a lot more data to analyze on the business side than the consumer side which is why [things like] the social graph is a little less relevant,” Breslow said.
In the end, lenders don’t need to go on a wild data goose chase to learn all about their prospective clients. Kabbage applicants for instance are asked to provide their online banking credentials in the very first step of the applications. “A lot of people would be surprised as to the amount of data borrowers are willing to share,” Petralia proclaimed. Indeed, many alternative business lenders and merchant cash advance companies are analyzing historical cash flow activity using third party aggregating services like Yodlee, something that requires the client’s credentials.
During Kabbage’s earlier demonstration, some members in the audience worried that factors such as deposit activity could be gamed. Petralia assured them that their algorithm was sophisticated enough to detect manipulation and at the same time explained that they analyzed far more than just deposit and balance history.
Perhaps all this technology though has gone overboard. Is it possible to predict performance just based on what the applicant says? Believe it or not, “the language someone uses is an indicator of default probability,” Stewart said. But even that kind of detection has become automated. “Lenddo uses semantic analysis. People tend to use different words when they’re desperate.”
Who knows, a year from now getting a loan might be as easy as picking up your phone and saying, “Siri, send money.” Just make sure to delete all the photos of you hanging out with criminals off your phone first. A lender might use them against you.
Last modified: April 20, 2019Sean Murray is the President and Chief Editor of deBanked and the founder of the Broker Fair Conference. Connect with me on LinkedIn or follow me on twitter. You can view all future deBanked events here.