Canada
Study Claims Canadian Market Needs to Improve Financial Literacy
January 24, 2020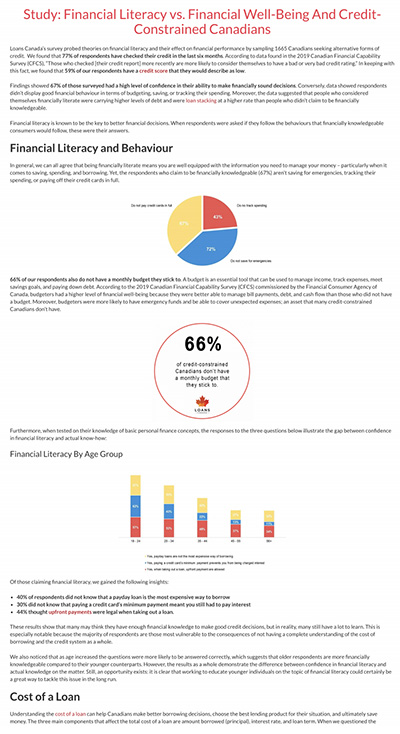 This week Loans Canada, a lead generation company, released a study documenting the disparities between perceived financial literacy and actual financial well-being. Surveying 1,665 Canadians, the report asserts that those individuals who claim to have a firm grasp of their financial situation may in fact be out of touch.
This week Loans Canada, a lead generation company, released a study documenting the disparities between perceived financial literacy and actual financial well-being. Surveying 1,665 Canadians, the report asserts that those individuals who claim to have a firm grasp of their financial situation may in fact be out of touch.
This being highlighted by major misunderstandings about how to budget for the future as well as a lack of education regarding loan repayments. 72% of the respondents said that they did not save for emergencies, 43% did not track their spending, and 66% do not stick to a monthly budget. Such budgetary omissions outline the potential for a large portion of the Canadian market to be in trouble should unforeseen expenses arise, and the fact that two thirds of the market aren’t even drawing up budgets is a cause for concern.
Such factors are made worse by the community’s seeming misinterpretations of loan terms. With 40% of the survey stating that they didn’t know payday loans were one of the most expensive ways to borrow money, 30% not understanding that paying the minimum amount of a credit card charge still meant you had to pay interest, and just over half of those surveyed were not able to identify the factors which affect the cost of loans, there appears to be a problem surrounding financial literacy and education of individuals regarding loans.
As well as these issues, there is the case of stacking loans, with the study indicating that the practice is not fully understood by Canadians and that the two top reasons for taking on multiple loans are for emergency costs (25%) and making ends meet (43%). Interestingly, the respondents who claimed to have the most confidence in their capacity to make financially sound decisions are more likely to be individuals who stack loans, leading them, inevitably, to have similar or more debt than those surveyed who said they were not confident in their financial decision-making ability.
Altogether, the study paints the picture of Canada as a market in need of further education. While financial literacy isn’t in crisis, the report points towards vulnerable sectors, such as such as those individuals with poor knowledge of loans and interest rates, as well as budgeting, are groups that need to develop a better understanding.
Open Banking: Canada Might Not Be Able to Make Up for Lost Time
January 22, 2020
Over the last two years, open banking has become a matter of public conversation in Canada. Most would agree there is overwhelming support for the implementation of an open banking regime. So why has nothing concrete happened yet?
2019 turned out to be an exciting, yet painfully underwhelming year for open banking in Canada. The news media finally caught on to the movement and started publishing stories on the rise of robo-advisor apps, or how small and medium-sized businesses would be impacted, and so forth. Experts and industry leaders pitched in with a massive volume of op-eds, most of which were in support of open banking, and with many deploring Canada’s slowness. Some came to our podcast to discuss their perspective (spoiler: customer-centricity is a very big theme.)
Another telling sign of the importance of open banking is the fact that at the federal level, both the legislative and executive arms of the government have become actively engaged in the public conversation. The Senate of Canada’s committee on Banking, Trade and Commerce produced a well-researched report — perhaps the most valuable contribution to the conversation. This report calls for swift action on the part of the federal government to advance a regulatory framework for open banking. In parallel, the Department of Finance’s appointed advisory committee on open banking held a consultation with key stakeholders and should publish its own report in the near future.
Even to a casual observer, there was an obvious sense that Canada is ready to embrace open banking.
But here’s the thing: despite all this work and evidence of widespread support, Canada didn’t move the needle on open banking in any concrete way.
Who’s leading?
The UK has already implemented a comprehensive open banking regime, and continental Europe is close behind. Dozens more countries are working toward their own versions. Among the various geographies moving in this direction, some are opting for a government-led approach, the UK probably being the best example. Others, like the US, tend to be more market-driven. In Canada, the main stakeholders are still largely hesitant about where to strike the balance between the two approaches — and the result is that so far, both have failed to provide the leadership that would allow open banking to move forward.
The Department of Finance’s advisory committee was tasked to study the “merits of open banking”. This line of inquiry feels very old, and for good reason: to question whether we should have open banking or not is a false debate, and a time-wasting rabbit hole. The real question Canada should be asking itself when it comes to open banking is, “what is the objective we want to achieve here?”
Let’s take a few steps back to realize just how important this question is.
The UK had a very clear vision for their open banking regime. The Competition and Markets Authority had assessed that the oligopolistic dynamics of the banking sector were putting consumers at a disadvantage. Thus, the UK set on their open banking journey with a very precise objective in mind: make it easier for consumers to switch providers. While some take great pride in criticizing the UK’s implementation — stating that its objective was either wrong, too narrow, or poorly executed — the fact remains that they are ahead of the pack. And the UK’s leadership in this area still persists, with the Financial Conduct Authority now studying the question of extending the current open banking regime into a holistic open finance regime.
 Meanwhile, in Canada, the government is trying to wrap its head around the big questions, such as the liability framework that should be put in place for an open banking regime to be viable. (In other words, in a system where financial services are decentralized, how do we go about making the consumer whole when something goes wrong?) However, without a decision on what end state we are looking to achieve with open banking, these conversations are doomed to keep looking exactly like they’re looking now: a bunch of market actors with conflicting interests pretending they know what’s best for consumers. Conversations happening in industry groups aren’t much more productive, with the “trench war” dynamics being the trend there as well.
Meanwhile, in Canada, the government is trying to wrap its head around the big questions, such as the liability framework that should be put in place for an open banking regime to be viable. (In other words, in a system where financial services are decentralized, how do we go about making the consumer whole when something goes wrong?) However, without a decision on what end state we are looking to achieve with open banking, these conversations are doomed to keep looking exactly like they’re looking now: a bunch of market actors with conflicting interests pretending they know what’s best for consumers. Conversations happening in industry groups aren’t much more productive, with the “trench war” dynamics being the trend there as well.
The irony is that the technical aspects of open banking can be dealt with easily. From a technical standpoint, financial data-sharing APIs have proven their effectiveness, and coming up with a shared technical standard should not be too difficult. The real challenge is coming up with a framework everyone — incumbents and new entrants alike — can rally behind, something industry groups have largely been ineffective at.
Canada’s highly concentrated financial services sector is a stable one, but incumbents are not likely to open themselves up to disruption. This is the part where bold political leadership is required.
The clock is ticking
Data sharing is nevertheless picking up, as 4 million Canadians (and counting) have made fintech apps a part of their financial lives. Consumers and businesses who want the benefits of on-demand data sharing must rely on the current generation of financial aggregators, like Flinks. This system may work as a de facto connectivity layer, but the lack of standards results in a clumsy patchwork of bilateral deals between aggregators and banks. It just isn’t a viable way to achieve an open banking regime that levels the playing field when it comes to data portability.
In its report, the Senate’s Committee on Banking, Trade and Commerce states that Canada “risks falling behind” if it fails to implement open banking, and that “without swift action, Canada may become an importer of financial technology rather than an exporter.” It is true that if we keep delaying open banking, our slowness will prove to be a very stingy and lasting price to pay for the Canadian society; this is why we need bold action now. We can’t afford the comfort of waiting until we’ve figured out the 100% perfect solution.
There’s nothing like a real-world example: 2020 opened with a seismic shift when financial giant Visa acquired Plaid, one of the largest US financial aggregators, for over five billion USD. This is hinting at a new phase where markets will consolidate around a few large players; Canada can either ride the tide or get towed under.
It’s time to be bold
In the end, what needs to happen for Canada to move forward with open banking?
Our financial services sector can be compared to those of the UK and Australia, where a few powerful banks control a very large portion of the market. In those two countries, open banking was designed to stimulate competition, and government action was necessary to get things moving.
Right now, the question politicians ought to ask shouldn’t be if — or even how — but why. A why will pave the way and provide a natural direction to sort out the how. In 2019, discussions around open banking lacked this fundamental feature: political leadership centered on a bold, ambitious, consumer-centric mission statement. A why.
So here’s one for 2020: open banking will increase consumers’ choice when it comes to financial services. That would be a good start — and while good is not perfect, it still beats nothing by a landslide.
Report Finds Canadian Alternative Lending Market Making Gains
January 8, 2020 A study released by Smarter Loans this week indicates that the Canadian alternative finance industry has grown since last year’s iteration of the report. Titled ‘The State of Alternative Lending in Canada 2019,’ the report highlights how the market has developed in regard to the age and gender of its customers, the level of trust in online lenders compared to financial institutions, as well as the levels of satisfaction felt by Canadians dealing with alternative funders.
A study released by Smarter Loans this week indicates that the Canadian alternative finance industry has grown since last year’s iteration of the report. Titled ‘The State of Alternative Lending in Canada 2019,’ the report highlights how the market has developed in regard to the age and gender of its customers, the level of trust in online lenders compared to financial institutions, as well as the levels of satisfaction felt by Canadians dealing with alternative funders.
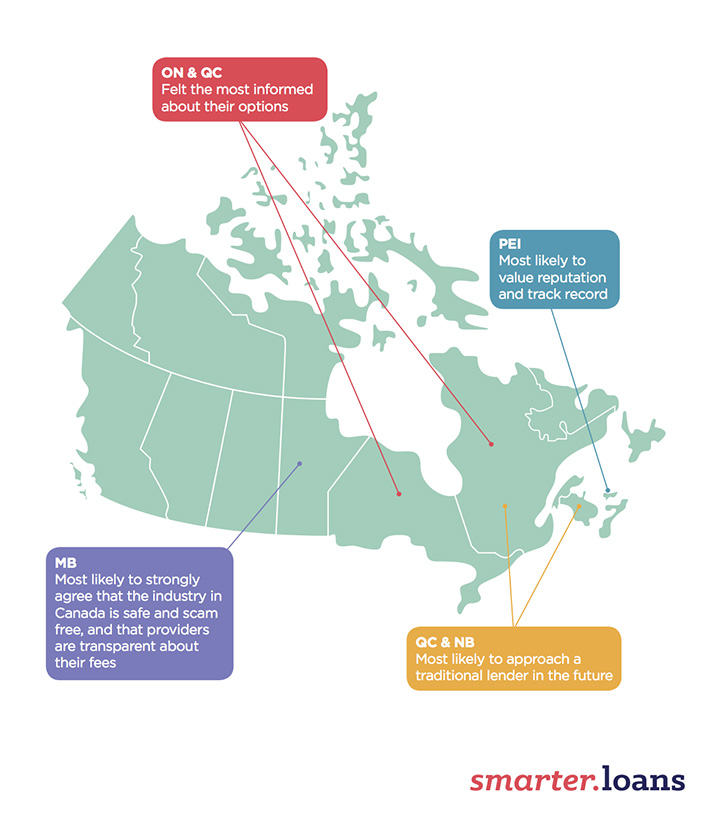
The first of these, regarding aspects of the customers’ identities, demonstrates that generational gaps are as wide as they’ve ever been amongst customers. Each age bracket questioned by the study showed differing priorities when seeking a loan. Generation Z, fitting in between those aged 18-24, paid attention to funders’ track records and reputation when looking for funding; whereas millennials (25-34) sought speedier applications and approvals. Generation X (45-54) however appeared more money-minded, with the priority being placed on terms and interest rates; and Baby Boomers (55-64) demonstrated a desire for having someone to talk to, putting customer service at the top of their list.
Vlad Sherbatov, Smarter Loans’ President and Co-founder, told deBanked that these differences can be summed up as the values each generation has developed through experience. Explaining that Gen Z is “all about the personal brand,” Sherbatov said, “People that are younger now really associate with the company they work for, they ask, ‘Am I aligned with or would I be embarrassed supporting this brand?’” While the Millennials’ response indicates a greater desire for results, “as the age progress the intent increases.” Gen X is “more educated and experienced people,” who appear to place the greatest importance on money; and Baby Boomers, the least digitally fluent group, just want the online applications to go smoothly and to have ready access to assistance.
As well as age, gender appeared to divide customers, with women more likely to spend more time researching loan providers than men; and more men saying that they were interested in approaching a traditional financial institution for a loan in the future, with half of them being of this opinion compared to just 39% of women. As well as this, it was found that women are more likely to find the application easier, but are less likely to be approved than men.
Regarding trust and transparency, roughly 70% of Canadians believe alternative finance to be a safe way of getting a loan. With 80% of customers feeling that they are informed enough of the industry’s practices and 69% saying that they believe online loan providers are transparent about their fees, interest rates, terms, and conditions.
According to Sherbatov, “this is a trend that’s been moving in a positive direction” over the years. With the 2018 version of this study emphasizing the need to build trust with Canadians to reduce that 30% which is holding out on, Sherbatov maintains the need to do more. “The more transparency from lenders, the more trustworthy it’ll be, the further the industry will advance.”
Customers appear to be mostly satisfied with the service they received from alternative lenders in 2019, with the average rating taken from the 2,415 respondents being 3.4 out of 5. This being a 0.2 bump up from last year’s score. Interestingly, one of the sectors reporting the highest levels of satisfaction were those customers who received payday loans, noting that they appreciated the speed with which they were approved.
Altogether, the report paints a picture of the Canadian scene as a market still in flux, where growth is happening, albeit slight, and both the customers and the lenders still have much to learn from each other.
Merchant Growth Partners with goeasy to Provide Funding via Physical Branches
December 11, 2019 This month Merchant Growth, the Vancouver-based alternative finance company, announced its partnership with goeasy Ltd. that will see Merchant Growth’s services being offered in goeasy branches throughout Canada. Beginning with British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan in 2019, Merchant Growth aims to have expanded to the remaining provinces in the first quarter of 2020.
This month Merchant Growth, the Vancouver-based alternative finance company, announced its partnership with goeasy Ltd. that will see Merchant Growth’s services being offered in goeasy branches throughout Canada. Beginning with British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan in 2019, Merchant Growth aims to have expanded to the remaining provinces in the first quarter of 2020.
Under the partnership, goeasy will receive compensation from Merchant Growth for all loans made through them while Merchant Growth will provide the capital.
“goeasy is a unique Canadian success and they’ve done that by being disciplined managers, by putting their customers first, and by building a great reputation for themselves in the industry,” said David Gens, Merchant Growth’s President and CEO. “And what we see in them is an ideal partner in that they have the market reach in terms of brand recognition and locations around the country.”
It is the latter of these factors that make the deal stand out. Given the industry’s standard of digital applications, goeasy and Merchant Growth’s return to brick and mortar branches that offer live human managers, clerks, and even physical paper, marks a turn back towards more historical methods of doing business.
Gens commented on this, stating that “there’s something to be said for face-to-face interactions and for that reason I don’t think you’re ever going to go down to having no bank branches … Having a physical location where you can chat with people about your financial needs is something that will always exist as far as I can see.”
The Current State of SME Lending in Canada
December 1, 2019 According to the latest statistics, there were 1.18 million employer businesses in Canada, with the majority of them located in the provinces of Ontario and Quebec.
According to the latest statistics, there were 1.18 million employer businesses in Canada, with the majority of them located in the provinces of Ontario and Quebec.
- 1.15 million (97.9%) represented small businesses
- 21.926 (1.9%) referred to medium-sized ventures
- Only 2.939 (0.2%) accounted for large corporations
Small and medium companies are blooming in Canada: they represent 99.8% of all businesses, and they are the heart of the local economy. However, these businesses are facing extreme challenges when it comes to raising capital – a crucial element of SME growth.
The Canadian banking sphere, dominated by five large banks, often overlooks these businesses. Banks in Canada typically require 32 articles of information when applying for a loan and still 78% of applications from SMEs are rejected. It is especially stressful for startups: you can’t get a loan unless you have customers, but you can’t start your business and get customers without a loan. Cash flow, on the whole, is a complex concept that may be confusing for small business owners, and this kind of financial exclusion only makes it worse. The problem is global, but this Catch-22 has given the green light to alternative lenders worldwide.
THE ALTERNATIVE
One of the alternative funding options for SMEs to bypass the banks and find the right level of capital that they need is called a merchant cash advance (MCA). MCAs aren’t loans. Instead, they represent the sale of a business’s future revenues in exchange for quick cash — the majority of applications are approved within 2 days. This way, a funder provides a lump sum payment with a predetermined percentage (the factor rate) of a merchant’s future credit or debit card sales — cash and check sales typically don’t qualify to be counted. The process goes on until the contractual terms are satisfied. The MCA industry is growing on Canadian soil, but since it is a relatively new domain, the sector remains heavily influenced by American providers, especially when it comes to business models and pricing. But domestic providers don’t see it as a threat. Bruce Marshall, VP of British Columbia-based Company Capital told deBanked in 2016 that “We are happy that some of the bigger US players are coming up here and they are spending millions of dollars on advertising. These companies raise awareness of the industry to a higher level and with us being a smaller company, we can ride on their coattails.”
The question of raising awareness of new technology is vital. In comparison to American SME owners, their Canadian colleagues are slower to adopt technology — for instance, only 27% say they currently use technology to analyze customer data. Another study by BDC claims that only 19% of Canadian businesses are digitally advanced.
On the other side, those established companies find the Canadian alternative lending market to be “a very manageable extension of the US market.” However, it’s a smaller market, and Canada’s geographical position (the majority of businesses are located in four main provinces out of thirteen) and regional differences play their part as well. For instance, because of the restrictions that require businesses to advertise and produce marketing materials in French, the majority of alternative lenders from the US don’t operate in Quebec.
RATES, COSTS, AND FIGURES
All in all, MCAs are slowly becoming a financing option for Canadian SMEs looking for quick cash. That “slowness” comes from a lack of understanding about how exactly merchant cash advances work. Some alternative funders take advantage of their non-bank status to neglect regulations that require clarity resulting in somewhat unethical lending practices. Because of this, a certain number of business owners still hesitate to take a chance on a merchant cash advance program.
MCAs in Canada are generally available to businesses that have a steady volume of credit card sales, such as retail stores or restaurants. The amount of personal and business information required when applying for an MCA is much lower in comparison to a regular bank loan application: the documentation generally includes proof of identity, bank statements, and business tax returns. Merchant cash advance rates and costs differ from provider to provider. As MCAs aren’t loans, there are no fixed amounts for repayment installments and no fixed terms either. Typically, the percentage of credit card sales taken to enable the transaction ranges from 5 to 10%. Some companies in Canada charge premiums on their cash advances (which can be as high as 30% or even more.)
THE CHALLENGE
The main challenge for Canadian MCA providers is the absence of reliable data necessary for making underwriting decisions. As previously mentioned, only a small group of large financial institutions dominate the market, so the data is available solely to a handful of businesses. The information obtained from credit bureaus doesn’t help either: in most cases, it isn’t complete for making a wise credit decision. “The availability and access to government and financial data are scarce in Canada compared to other markets,” said Jeff Mitelman, the former CEO of Thinking Capital in an interview with deBanked in a past interview. “Most of the data relationships that fintech companies rely on, need to be developed on a one-to-one basis and is often proprietary information.”
When it comes to the process of underwriting, the availability of data presented in the proper format is a crucial factor. It provides the full picture and saves an enormous amount of time for risk officers. “We pay a lot of attention to our underwriting and decision-making process because if we make a mistake, we can lose a lot of money,” Andrew D’Souza, the CEO of Clearbanc, told TechCrunch.
At the moment, the financial data available to Canadian alternative lenders is meager and needs improvement. Another issue is the legislation that varies with each province. Many alternative lenders find the Canadian rules and regulations that govern the industry rather unclear. However, those challenges are associated with a growing market and emerging ecosystem. One way or another, the business loan landscape has changed for good, and alternative financing methods have captured much attention, with giants like PayPal stepping in the game.
THE NEXT STEP
As the industry is new, and has lots of challenges, the banking sphere and fintechs are turning to partnerships accelerating online lending to small business members. It makes perfect sense to MCA providers to license their automated platforms, banks, and credit unions. Traditional players are familiar with regulations and have data for fine-tuned underwriting, while fintech providers bring innovative technology and customer experience. “We saw that Canada is ripe for technology but the differences in regulation among other things made us go the partner route,” said Peter Steger, the head of business development at Kabbage, to deBanked – a perfect illustration of the growing partnership trend. These mutual interests create a lot of business opportunities, and that’s a good sign for all parties involved.
When small business owners need financing, timing is essential. Small and medium businesses are vital to the Canadian economy, so for them, the proper financial support means fast and convenient access to credit. In the new fintech-driven reality, applications should be completed within thirty minutes, decisions made within hours, and funds deposited in the applicant’s bank account within days. Canadian small businesses contribute around 30% of the total GDP, so the need for simple finance is acute. The technology has already made small business lending more accessible, and over time, financing alternatives such as MCA will become mainstream.
Fast and Furious Funders – At The Canadian Lenders Association’s Venture Debt Summit
November 30, 2019Fast and Furious Funders was the name of a panel at the Venture Debt Summit hosted by the Canadian Lenders Association on October 23, 2019. Panelists included:
- Karanjit Bhugra, Managing Director, Deloitte Corporate Finance
- Jyotin Handa, Director of Finance, Espresso Capital
- Tanay Delima, Co-Founder, Clearbanc
- Keren Moynihan, Co-Founder, Boss Insights
You can watch the video of the panel below:
Canadian Lenders Summit Recap
November 23, 2019 The Canadian Lenders Association’s largest annual event brought together hundreds of executives from the fintech and lending industries. It was hosted at MaRS, a dedicated launchpad for startups in Downtown Toronto that occupies more than 1.5 million square feet and is home to more than 120 tenants, many of which are global tech companies.
The Canadian Lenders Association’s largest annual event brought together hundreds of executives from the fintech and lending industries. It was hosted at MaRS, a dedicated launchpad for startups in Downtown Toronto that occupies more than 1.5 million square feet and is home to more than 120 tenants, many of which are global tech companies.
After OnDeck Canada CEO Neil Wechsler was introduced as the new chairman of the association, the day kicked off with a presentation by Craig Alexander, the Chief Economist of Deloitte Canada. Alexander explained that after some major warning signs sounded off late last year and early this year, Canadian growth and positive economic indicators have returned. He opined that politics in Canada and the United States will play a strong role in the economic outcomes of both countries going forward.
Panels on a variety of topics dominated the rest of the day with an interlude keynote from author Alex Tapscott who spoke about the financial services revolution.
The sessions concluded with an award ceremony focused around the Top 25 Company Leaders in Lending and the Top 25 Executive Leaders in Lending. The Canadian Lenders Association will make videos of the sessions available online. deBanked was in attendance.
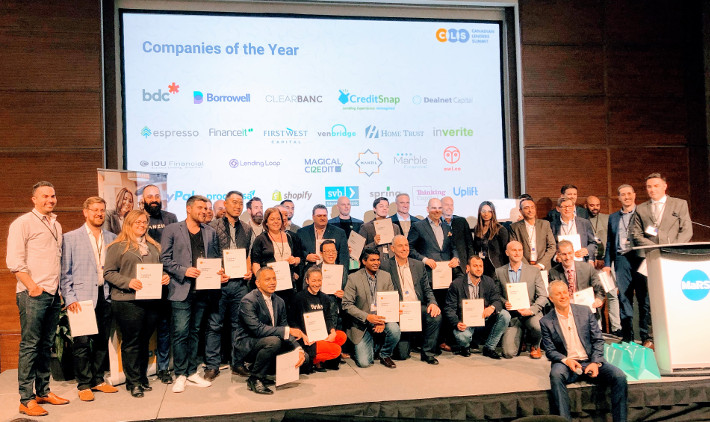

2019 Top 25 Executive Leaders in Lending – Canadian Lenders Association – Presented By BMO
November 11, 2019 The Canadian Lenders Assocation (CLA) received 124 nominations for these awards from leaders in lending across the country. The CLA’s goal is to support access to credit in the Canadian marketplace and champion the companies and entrepreneurs who are leading innovations in this industry.
The Canadian Lenders Assocation (CLA) received 124 nominations for these awards from leaders in lending across the country. The CLA’s goal is to support access to credit in the Canadian marketplace and champion the companies and entrepreneurs who are leading innovations in this industry.
The Top 25 finalists in this report represent various innovations in the borrower’s journey from innovations in artificial intelligence powered credit modelling to breakthroughs in consumer identity management using blockchain technologies. These finalists also represent solutions for a wide spectrum of borrower maturity and needs, ranging from consumer credit rebuilding all the way to senior debt placements for global technology ventures.
See The Leading Companies Report Here
See The Leading Executives Report Here
 |
Mark Cashin
CEO of myBrokerBee | Ontario After a career in commercial finance and being CEO of Transpor, Mark Co-founded myBrokerBee a mortgage broker platform that provides transparency to private lenders and their clients. |
 |
Avinash Chidambaram
CEO of Ario Platform | Ontario Through his experience as Product lead at Interac and Blackberry, Avinash has helped bring together an accomplished and talented group of experts in Data Science, Machine Learning, Security, Software Development to successfully develop this banking services software platform Ario. |
 |
Evan Chrapko
CEO of Trust Science | Alberta Evan is the founder and CEO of Trust Science, a leader in organizing alternative credit data. As a saas founder and CEO, Evan has done over 500mm in startup exits. |
 |
Kevin Clark
President of Lendified | Ontario Kevin is a recognized leader in the financial services industry with over 30 years of experience. Kevin has helped create the voice of Canada’s SME lending ecosystem through his leadership of Lendified and the CLA. |
 |
Jerome Dwight
VP of Cox Automotive | Ontario Jerome established Nextgear Capital in Canada to become the largest specialty finance company in the automotive sector. Jerome is a Globe & Mail 40 under 40 winner and previously lead RBC’s international wealth management, private banking and asset servicing business. |
 |
Saul Fine
CEO of Innovative Assessmer | Israel Saul is a licensed organizational psychologist and psychometrician, and a former lecturer in psychology at the University of Haifa. Saul is a global leader in the use of psychometric data for credit scoring and financial inclusion. |
 |
David Gens
CEO of Merchant Growth | BC David is the Founder and CEO of Merchant Growth, which grew from its humble beginnings in his apartment to offices in both Toronto and Vancouver. David now leads one of Canada’s largest online small business finance companies. |
 |
Bryan Jaskolka
COO of CMI | Ontario Nominated for the 2018 Mortgage Broker of the Year, Bryan Jaskolka is an expert in Canadian mortgage financing with a particular focus on the alternative lending space and mortgage investing. |
 |
Peter Kalen
CEO of Flexiti | Ontario Peter is a leader in Canada’s retail financing market. Before founding Flexiti, Peter was in senior leadership positions at Citi, PC Financial, and Sears Canada. Flexiti was recently named #7 on the Deloitte Fast50. |
 |
Yves-Gabriel Leboeuf
CEO of Flinks | Quebec Yves-Gabriel Leboeuf is the co-founder and CEO of Flinks. Under his leadership, Flinks has become a Canadian leader in banking data enablement. |
 |
Derek Manuge
CEO of Corl | Ontario Derek, also known as the “the quant from Canada” is the founder of the data-driven venture firm, Corl. Corl is one of Canada’s leaders in the use revenue-share financing models. |
 |
Keren Moynihan
CEO of Boss Insights | Ontario Keren Moynihan is co-founder and CEO of Boss Insights, a company that uses big data and AI to accelerate lending from months to minutes. With a Joint JD/MBA, Keren has a diverse background as a commercial banker, wealth manager and former founder of an impact startup. |
 |
Jason Mullins
CEO of Goeasy | Ontario Jason is President and CEO of goeasy, a publicly listed consumer lender. Jason has lead the company to become one of the largest and most innovative lenders in the country. |
 |
Paul Pitcher
CEO of SharpShooter Funding | Ontario After founding First Down Funding, an alternative lending firm for SMEs in Baltimore, Paul expanded his business to Canada through the subsidiary Sharpshooter Funding. |
 |
Brendan Playford & Cate Rung
Co-Founders of Pngme | USA Cate, ex-Uber and Brendan, a blockchain and agro-finance entrepreneur are the co-founders of Pngme, an alternative lending platform for financial institutions in emerging markets who serve Micro, Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises. |
 |
Wayne Pommen
CEO of Paybright | Ontario Wayne is the President and CEO of PayBright. Wayne is also a director of IOU Financial Inc and of HBC. Previously, Wayne was a Principal at TorQuest Partners, one of Canada’s leading private equity firms, and a management consultant with Bain & Company in the UK, the US, and Canada. |
 |
Adam Reeds
CEO of Ledn | Ontario Adam is a pioneer and thought leader in the digital asset backed lending space. Ledn is focused on building innovative financial products in the emerging digital asset space, with a focused mission to help people save more in bitcoin. |
 |
Adam Rice
CEO of LoanConnect | Ontario Adam has played a pivotal role in building one of the largest online markets in Canada for unsecured loans. |
 |
Mark Ruddock
CEO of BFS Capital | Ontario Mark is an experienced international CEO with two successful exits and over 20 years of experience at the helm of VC backed technology and fintech startups. In 2019 Mark announced BFS Capital’s expansion to Canada with a new 50 engineer data science hub in the heart of Toronto. |
 |
Vlad Sherbatov
President of Smarter Loans | Ontario Vlad Co-founded Smarter Loans in 2016 with the goal of helping Canadians make smarter financial decisions. Since then, Vlad has grown the platform into one of the go-to resources for Canadian borrowers. |
 |
Steven Uster
CEO of FundThrough | Ontario Steven is the Co-Founder & CEO of FundThrough, an invoice funding service that helps business owners eliminate “the wait” associated with payment terms by giving them the power and flexibility to get their invoices paid when they want, with one click, and in as little as 24 hours. |
 |
Dmitry Voronenko
CEO of Turnkey Lender| Singapore Dmitry, CEO and Co-founder of TurnKey Lender, holds a PhD in Artificial Intelligence. Dmitry was recently named SFA’s Fintech Leader of the year. |
 |
Neil Wechsler
CEO of Ondeck Canada | Quebec Neil briefly practiced law before becoming President and CEO of Optimal Group Inc. where he grew the company from a start-up to a leading NASDAQ-listed self-checkout and payments company. Neil later co-founded Evolocity, which in 2019 became OnDeck Canada. |
 |
Michael Wendland
CEO of Refresh | BC Michael has led Refresh Financial’s rapid growth since its founding in 2013, including a recent ranking of number 40 on Deloitte’s Fast 500. |