 |  |
Related Headlines
| 09/25/2018 | Meet Central Diligence Group Oct 4th |
Related Videos
Live 3/23 - Central Diligence Group | A Word From Central Diligence Group |
Stories
Central Diligence Group is a Sponsor of deBanked CONNECT – San Diego
September 25, 2018Central Diligence Group is a sponsor of deBanked CONNECT San Diego. The half-day event for funders, lenders, brokers and industry professionals is being held at the Andaz on October 4th!

Check out photos from deBanked’s past CONNECT event in Miami
Arrangements for Nick Gregory of CDG: Rest in Peace
August 29, 2022Nick Gregory, a co-founder and partner of both Central Diligence Group and Capital Dude, passed away suddenly last Thursday. Gregory was a well-known and beloved 16-year veteran of the small business finance industry. If you’d like to pay your respects, please take note of the following arrangements:
Wake Location:
Roslyn Heights Funeral Home
75 Mineola Ave
Roslyn Heights, NY 11577
Tues August 30th: 3-5PM, 7-9PM
Wed August 31st: 3-5PM, 7-9PM
Mass:
Thurs September 1st, 10AM:
St. Mary’s Roman Catholic Church
110 Bryant Ave, Roslyn, NY 11576
-Funeral Procession to Cemetery-
Burial:
11:30-11:45AM:
Cemetery of the Holy Rood
111 Old Country Rd, Westbury, NY 11590
What The “Capital Dude” Said About Experience, Success, and the Future
August 18, 2021 Coming in at rank #1,044 on the 2021 Inc 5000 list was a small business finance provider with a whimsical name, Capital Dude. Having some common ownership overlap with another Inc ranked company, Central Diligence Group (#2,893), the Dude told deBanked that they didn’t shut down or pause funding throughout 2020. In fact, they continued to grow.
Coming in at rank #1,044 on the 2021 Inc 5000 list was a small business finance provider with a whimsical name, Capital Dude. Having some common ownership overlap with another Inc ranked company, Central Diligence Group (#2,893), the Dude told deBanked that they didn’t shut down or pause funding throughout 2020. In fact, they continued to grow.
“We really have to attribute the company’s growth to our hardworking and efficient team that made sure we didn’t miss a beat while having to work remote,” said company partner Andrew Hernandez.
The name, Capital Dude, was chosen to convey an easy process to their partners and clients, the company says, while at the same time being compatible with a mascot they had in mind. The Capital Dude himself is a superhero in a green suit with the letters “CD” emblazoned on his chest. He’s also got a red cape and a flashy smile.
Behind the optics, however, is a seasoned team.
“We got started in the industry during the ’08 – ’09 recession,” Hernandez said, “so when you experience getting started during a downturn, you quickly realize that the only way to keep going is to stick to your principles while continuously taking inventory of the ongoing situation and making any necessary changes quickly in order to protect the portfolio. While both downturns were very different in how they played out, applying that previous experience to the past 18 months has been interesting as we have seen a lot of similarities that are very measurable.”
Central Diligence Group, meanwhile, has gotten repeat recognition on the Inc 5000 list.
“CDG offers consulting and underwriting services to other alternative financing companies in the industry,” Hernandez explained. The “short term plan is to scale out this portion of the business in 2022 via licensing of our platform to funders, funds, accredited investors, etc.”
The companies are currently in the process of moving to a new office and they expressed that they are “very bullish on the future” and plan to increase their headcount and continue to grow.
Small Business Finance on the 2021 Inc 5000 List
August 17, 2021Here’s where alternative small business finance ranks on the Inc 5000 list for 2021:
| Ranking | Company Name | Growth |
| 44 | Crestmont Capital | 7,404% |
| 1044 | Capital Dude | 463% |
| 1221 | Fountainhead | 394% |
| 2298 | Bankers Healthcare Group | 186% |
| 2427 | Fund&Grow | 173% |
| 2628 | Channel Partners Capital | 155% |
| 2803 | PIRS Capital | 142% |
| 2893 | Central Diligence Group | 135% |
| 3005 | ApplePie Capital | 127% |
| 3027 | Nav | 126% |
| 3365 | Onset Financial | 105% |
| 3394 | OTR Capital | 104% |
| 3547 | Forward Financing | 96% |
Did we forget you? Let us know at info@debanked.com
Where Fintech Ranks on the Inc 5000 List for 2020
August 12, 2020Here’s where fintech and online lending rank on the Inc 5000 list for 2020:
| Ranking | Company Name | Growth |
| 30 | Ocrolus | 7,919% |
| 46 | Yieldstreet | 6,103% |
| 351 | Direct Funding Now | 1,297% |
| 402 | GROUNDFLOOR | 1,141% |
| 486 | LoanPaymentPro | 946% |
| 534 | LendingPoint | 862% |
| 539 | OppLoans | 860% |
| 566 | dv01 | 830% |
| 647 | Fund That Flip | 724% |
| 1031 | Fundera | 449% |
| 1035 | Nav | 447% |
| 1053 | Fundrise | 442% |
| 1103 | Bitcoin Depot | 409% |
| 1229 | Smart Business Funding | 365% |
| 1282 | Global Lending Services | 349% |
| 1360 | CommonBond | 327% |
| 1392 | Forward Financing | 319% |
| 1398 | Fundation Group | 318% |
| 1502 | Fountainhead Commercial Capital | 293% |
| 1736 | Seek Capital | 246% |
| 1746 | PIRS Capital | 244% |
| 1776 | Braviant Holdings | 240% |
| 1933 | Choice Merchant Solutions | 218% |
| 2001 | Fundomate | 212% |
| 2257 | Lighter Capital | 185% |
| 2466 | Bankers Healthcare Group | 167% |
| 2501 | Fund&Grow | 165% |
| 2537 | Central Diligence Group | 162% |
| 2761 | Lendtek | 145% |
| 3062 | Shore Funding Solutions | 127% |
| 3400 | Biz2Credit | 110% |
| 3575 | National Funding | 103% |
| 4344 | Yalber & Got Capital | 76% |
| 4509 | Expansion Capital Group | 70% |
Underwriting 101—Veteran Funders Share Tools of the Trade
August 12, 2018For brokers, funding partnerships are critical to success. But making the most of these connections can be elusive.
“Transparency, efficiency and a thorough scrubbing on the front end can help the whole process,” says William Gallagher, president of CFG Merchant Solutions, an alternative funder with offices in Rutherford, N.J. and Manhattan.

Gallagher recently moderated an “Underwriting 101” panel at Broker Fair 2018, which deBanked hosted in May. The panel featured a handful of representatives from different funding companies discussing various hot-button items including striking the proper balance between technology and human underwriting, trade secrets of the submission process and stacking. Here are some major takeaways from that discussion and from follow-up conversations deBanked had with panel participants.
Each funder has slightly different processes and requirements. Brokers need to understand the different nuances of each firm so they know how to properly prepare merchants and send relevant information, funders say.
Many brokers sign up with funders without delving deeper into what the different funders are really looking for, says Jordan Fein, chief executive of Greenbox Capital in Miami Gardens, Fla., that provides funding to small businesses.

For example, there are a growing number of companies that rely more heavily on advanced technology for their underwriting, while others have more human intervention. Brokers need to know from the start what the funder’s underwriting process is like—the nitty gritty of what each funder is looking for—so they can more effectively send files to the appropriate funder.
“They will look poor in front of the merchant if they don’t really know the process,” Fein says.
Certainly, it’s a different ballgame for brokers when dealing with funders that are more human based versus more automated, says Taariq Lewis, chief executive and co-founder of Aquila Services Inc., a San Francisco-based company that offers merchants bank account cash flow analysis as well as funding that ranges from 70 days to 100 business days.

At Aquila, the process is meant to be totally automated so that brokers spend more time winning deals faster, with better data to do so. This means, however, that some of the underwriting requirements differ from some other industry players. Aquila’s most important requirement is that a merchant’s business is generally healthy and shows a positive history of sales deposits. Other funders require documents and background explanations, whereas Aquila strives to be completely data-driven, Lewis says. These types of distinctions can be important when submitting deals, funders say.
Stacking is another example of a key difference among funders that brokers need to understand. It’s a controversial practice; some funders are open to stacking, while others will only take up to a second or third position; a number of funders shy away from the practice completely. Brokers shouldn’t waste their time sending deals if there’s no chance a funder will take it; they have to do their research upfront, funders say.
Most times, brokers “don’t invest enough time to understand the process,” Fein says.
Some brokers may feel competitive pressure to sign up with as many funders as possible, but it can easily become unwieldy if the list is too long, funders say. Better, they say, to deal with only a handful of funders and truly understand what each of them is looking for.

“There are brokers that deal with 20 [funders], but I don’t think it’s a good, efficient practice,” says Rory Marks, co-founder and managing partner of Central Diligence Group, a New York funder that provides working capital for small businesses.
He suggests brokers select funders that are easy to work with and responsive to their phone calls and emails. Not all funders will pick up the phone to speak with brokers who have questions, but he believes his type of service is paramount, he says. “It’s something we do all the time,” he says.
He also recommends brokers consider a funder’s speed and efficiency of funding as well as document requirements and their individual specialties. There are plenty of funders to choose from, so brokers shouldn’t feel they have to work with those that are more difficult, he says.
To prevent a broker’s list from becoming too unwieldy, Gallagher of CFG Merchant Solutions suggests brokers have two to three go-to funders in each category of paper from the highest quality down to the lowest. Having a few options in each bucket allows greater flexibility in case one funder changes its parameters for deals, he says.
Brokers “sometimes just shotgun things and throw things against the wall and hope they stick,” Gallagher says. Instead, he and other funders advocate a more precise approach –proactively deciding where to send files based on what they know about the merchant and research they’ve done on prospective funders.
It used to be that when sending files to funders, brokers would provide some background on the company in the body of the email. This was helpful because even a few sentences can help funders gain some perspective about the company and better understand their funding needs, says Fein of Greenbox Capital.
These days, however, Fein says he’s getting more emails from brokers that simply request the maximum funding offer, without providing important details about the business. The financials on ABC importing company aren’t necessarily going to tell the whole story because funders won’t know what products they import and why the business is so successful and needs money to grow. Providing these types of details could help sway the underwriting process in a merchant’s favor. Brokers don’t have to say a lot, but funders appreciate having some meaty details. “A few sentences go a long way,” Fein says.
Many brokers make the mistake of overpromising what they can get for merchants and how long the process could take, funders say. Both can cause significant angst between merchants and brokers and between brokers and funders.
If a company is doing $15k in sales volume and asking for $50k in funding, the broker should know off the bat, the merchant is not going to get what he wants, says Marks of Central Diligence Group. By managing merchant’s expectations, brokers are doing their clients—and themselves—a favor. Why waste time on deals that won’t fund because they are fighting an uphill battle? Brokers shouldn’t knowingly put themselves in the position of having to backtrack later, Marks says.
Instead, explain to the merchant ahead of time he’s likely to receive a smaller amount than he’d hoped for. To show him why, walk the merchant through a general cash flow analysis using data from the past three to four months, says Gallagher of CFG Merchant Solutions. This will help merchants understand the process better, and it can help raise a broker’s conversion rate, he says.
“It’s about setting realistic expectations,” Marks says.
Sometimes brokers take only a cursory look at a merchant’s financials, and because of this, they overlook important details that can delay, significantly alter, or sink the underwriting process, funders say.

Heather Francis, founder and chief executive of Elevate Funding in Gainesville, Fla., offers the hypothetical example of a merchant who has total deposits of $80k in his bank account. On its face, it may look like a solid deal and the broker may make certain assurances to the merchant. But if it comes out during underwriting that most of the deposits are transfers from a personal savings account as opposed to sales, there can be trouble. Based on the situation, the merchant may only be eligible for $30k, but yet the owner is expecting to receive $80k based on his discussions with the broker. Now you have an unhappy merchant, a frustrated broker and a funder who may be blamed by the merchant, even though it’s really the broker who should have dug deeper in the first place and then managed the merchant’s expectations accordingly. “We see that a lot,” says Francis.
To get the most favorable deals for merchants, some brokers only present the rosiest of information in the hopes that the funder won’t discover anything’s amiss. Several panelists expressed frustration with brokers who purposely withhold information, saying it puts deals at risk and makes the process much less efficient for everyone.
Marks of Central Diligence Group offers the hypothetical example of a merchant whose sales volume dipped in two of the past six months. To push the deal through, a broker might submit only four months of data, hoping the funder doesn’t ask about the other two months. Some funders might accept only four statements, but other shops will want to see six. If a funder then asks for six, the broker’s omission creates unnecessary friction, he says.
Funders say it’s better to be upfront and disclose relevant information such as sales dips or some other type of temporary setback that weighs a merchant’s financials. Kept hidden, even small details could easily become game-changers—or deal-breakers—a losing proposition for merchants, brokers and funders alike.
“If we have the full story upfront and we’re going in eyes wide open, we can look at the file in a little bit of a different way,” says Gallagher of CFG Merchant Solutions.
Why Small Businesses Sought Financing in 2017, and Why They Were Denied
May 24, 2018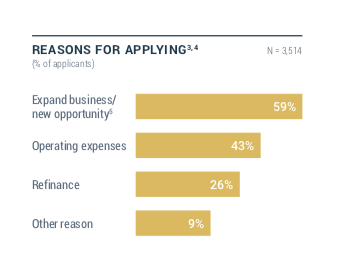 Nearly 60 percent of small businesses applied for financing in 2017 because they wanted to expand their business or pursue new opportunities, according to the latest report by the Federal Reserve. Forty-three percent of small businesses sought financing for operating expenses while 26 percent sought capital for refinancing. Nine percent had a different reason.
Nearly 60 percent of small businesses applied for financing in 2017 because they wanted to expand their business or pursue new opportunities, according to the latest report by the Federal Reserve. Forty-three percent of small businesses sought financing for operating expenses while 26 percent sought capital for refinancing. Nine percent had a different reason.
Of course, not all applications are funded. Forty-six percent of small businesses received all the financing they sought, 12 percent received most (more than 50 percent) of it, 20 percent received some (less than 50 percent) of the financing they desired and 23 percent were denied financing altogether.
Of the reasons why merchants were denied funding, “Having insufficient credit history” ranked number one, according to the report. A very close second was “Having insufficient collateral,” followed by “Having too much debt already.” After that, in descending order, came “Low credit score,” “Weak business performance” and “Other.”
The “Having insufficient collateral” category does not apply for MCA financing, but the other categories do. According to Nick Gregory, founding partner at Central Diligence Group, which provides MCA underwriting services, “Having too much debt already” is perhaps the main reason why merchants seeking cash advances get declined.
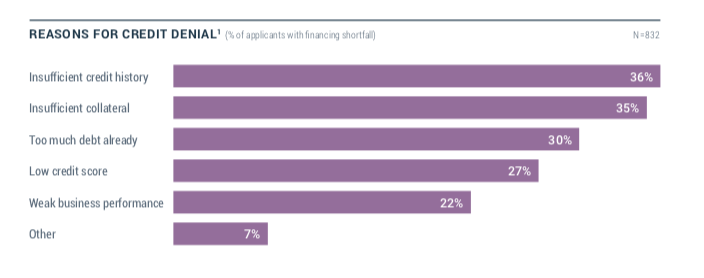
“A lot of times the merchants are overleveraged,” Gregory said.
He explained that if a merchant also has something like two MCA arrangements (or positions) already, that merchant likely has taken on too many contractual obligations which will often be a reason to decline the application. In Gregory’s experience, another common reason for declining an MCA financing application is “Weak business performance.”
Contradictory to the Federal Reserve report’s top reason for denying financing to a small business borrower, Gregory said that “Having insufficient credit history” is seldom a reason to deny MCA financing. This disconnect likely comes from the fact that the report includes all types of small business financing, with MCA accounting for just seven percent. The number maybe seem small, but it continues to increase while small business applications for factoring have decreased.
The Underwriters – How A Small Team Is Turning Underwriting Into Big Business
March 13, 2018
A keen eye can spot a good deal. And for New York-based Central Diligence Group, an underwriting-focused company founded in 2015 by four partners, it has been a boon for business. The company has lately been providing its underwriting expertise to a wider variety of clients, including some outside the MCA space.
“We started to gear towards a more underwriting-centric model [where] a deal would come in, we underwrite it once, we assess the risk, we determine what box it would fall under and where it would qualify, and depending on what that pedigree of information [was], we would essentially [fulfill] the full underwriting [job,]” said Nick Gregory, one of the founding partners at Central Diligence.
Initially, the company provided underwriting services mostly to smaller funders, syndication brokers and ISO clients that service MCA merchants in the construction and trucking businesses, among others. But close to three years later, its roster of clients is far more diverse.
Over the past six to eight months, Central Diligence has been working with a west coast-based credit card processing company with a portfolio of over 100,000 clients, according to Andrew Hernandez, another Central Diligence partner. The credit card processing company has just built out its own MCA product, but they don’t have an underwriting team, which is where Central Diligence comes in. Hernandez said that this company, the identity of whom he could not disclose, just renewed its contract with them.
 Another unique client is an institutional investor, with offices in New York and Dallas, that just formalized a new working relationship with Central Diligence over the last week to go beyond just underwriting and into the realm of funding and servicing. According to Hernandez, this client is looking to make investments in MCA at the higher end of the market.
Another unique client is an institutional investor, with offices in New York and Dallas, that just formalized a new working relationship with Central Diligence over the last week to go beyond just underwriting and into the realm of funding and servicing. According to Hernandez, this client is looking to make investments in MCA at the higher end of the market.
“In our space, $50,000 to $250,000 is pretty easy to come by, but $250,000 to $1 million, not so much,” Hernandez said. “So they see that there’s a gap with small businesses…and they’re using us to do [due] diligence [on companies.]”
Finally, Central Diligence is finishing an agreement with another unconventional client, an overseas mortgage company with interest in MCA. According to Hernandez, it is looking to execute a kind of beta test in the U.S. and then take the business model to Europe if it works.
In addition to the four founding partners, who work as underwriters, there are four additional underwriters and two junior underwriters for a total of ten on staff.
Hernandez attributes these new opportunities to the reputation they have built in the MCA space, including the 10+ years of experience that each of the founding partners have.
“Because of our experience and history in the space, a lot of our relationships have been built because of our credibility,” Hernandez said. “That’s the most important.”

See Post... central diligence group and forward financing are must adds. great companies run by good people, , thanks! forward put a pause so will see... |
See Post... central diligence group and forward financing are must adds. great companies run by good people... |
See Post... central diligence group they are my go to. great company with good people.... |
































