Archive for 2021
StreetShares Discontinues Veteran Business Bonds
February 3, 2021StreetShares, the former online lender that pivoted to Lending-as-a-Service in October, is no long offering its veteran business bond program as a result.
A note on its website says:
“Thank you Veteran Business Bond investors! We have achieved our Bond funding needs. As a result, we have discontinued our offering of Veteran Business Bonds. New Bonds are no longer available for purchase or investment. Your current Bonds continue to earn 5% annual interest. Investors are able to log in to access their accounts.“
Earnings Week: PayPal
February 3, 2021PayPal held their earnings results for Q4, describing its strongest year in history by chief executive Dan Schulman.
In Q4 alone, PayPal added 16 million net new million active customers and 1.4 million new merchants and raised $6 billion in revenue. That brings the total to 377 million new users for the entire year.
After adding cryptocurrency to the platform, Schulman said that users that bought virtual assets log in twice as frequently as they did before.
“We have seen an exceptional response to pour crypto launch,” Schulmann said. “The crypto volume traded on our platform greatly exceeded our projections.”
The payments by-now-pay-later product added raised $750 million in the last quarter.
An Amazon Capital Lending Loan
February 2, 2021Amazon’s small business lending business is no small operation. deBanked recently viewed a loan agreement between Amazon Lending and an Amazon seller in which the seller received a loan of $300,000 at an annual interest rate of 15.99%.
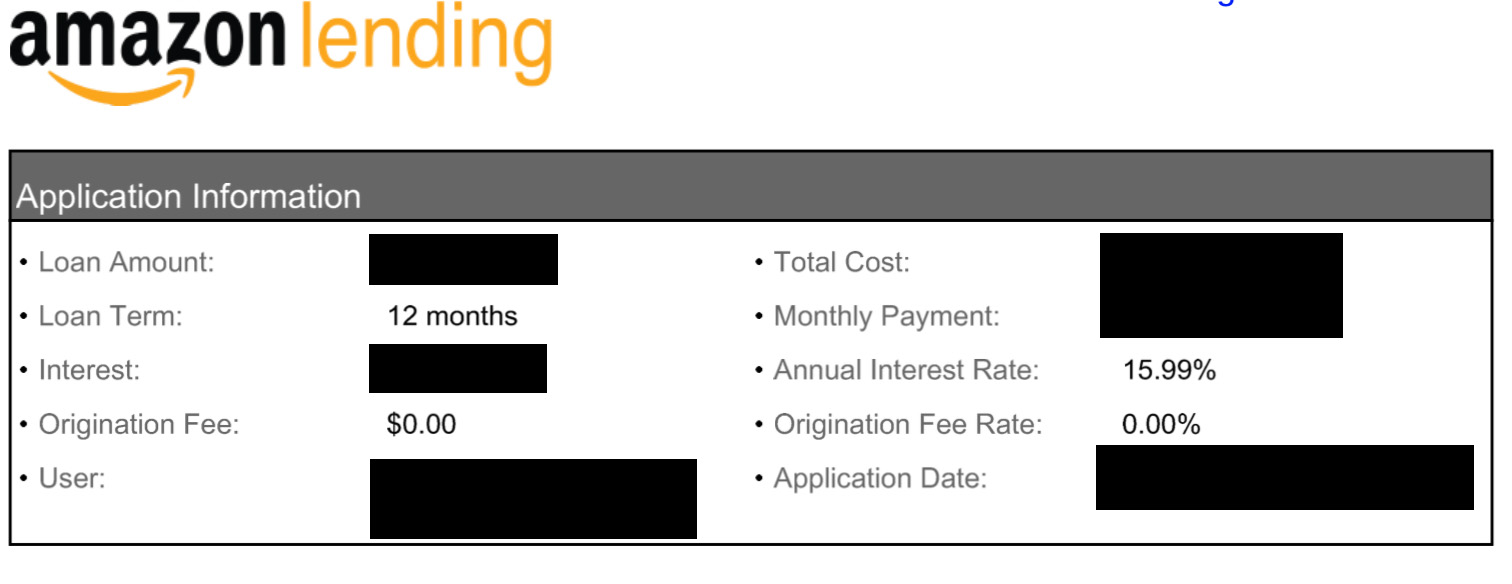
In 2019, we estimated that the company had originated $1.5B in small business loans, placing them in the #5 slot on our list, but the company is possibly on track to be #1.
Super Bowl Sunday: Battle of the Mortgage Brokers
February 2, 2021 This Sunday in Tampa Bay, the Chiefs, and the Buccaneers will duke it out, while a second mortgage-based rivalry plays out in the ads between plays.
This Sunday in Tampa Bay, the Chiefs, and the Buccaneers will duke it out, while a second mortgage-based rivalry plays out in the ads between plays.
A year ago, millions watched as Rocket Mortgage and United Wholesale Mortage (UWM) went head-to-head with competing multi-million-dollar ads. This year, they will both return, but it looks like they might play nice after a grueling pandemic.
Last year, Rocket appeared for their third consecutive Super Bowl, but then in an upset came the #BrokersAreBetter ad campaign. UMW called out their biggest competitor: “Playing with rockets is great when you’re a kid, but when it’s time to get a mortgage, you quickly realize a rocket is complicated and expensive,” and promoted FindAMortgageBroker.com.
It was a jab that earned millions of tweets, but this year Rocket has a chance to reply, and “double down” with two ads, this time highlighting local brokers as well. Rocket Companies today launched a national mortgage broker directory on its website.
“The directory not only includes the 43,000 individual loan officers who work with us but every mortgage broker in the country,” said Austin Niemiec, the executive vice president of Rocket Pro TP, in a statement. “This new resource is not about us; it’s about giving consumers more choice and assuring they know how an independent loan officer in their community can help them.”
UWM is also running an ad showing an imaginary tinder-swiping house hunting app, again featuring the FindAMortgageBroker.com directory.
“We believe we’re the one genuine partner of mortgage brokers nationwide,” said Sarah DeCiantis, chief marketing officer of UWM, in a statement. “We thought this ad would not only be relatable and entertaining given the pandemic’s acceleration of online dating but also educate consumers that brokers are their number one resource for finding a mortgage that fits their financial situation.”
Both firms are deciding to buy ads while other major brands are pulling out; For example, Budweiser’s decision to put ad money toward covid vaccine distribution. These brands will be saving money, as a 30-second spot during the Super Bowl runs for an estimated $5.5 million, the AP reports.
Next year’s Super Bowl 56, will be played in SoFi Stadium.
The Pain in America’s Food Supply Chain
January 29, 2021 It was last November, Mark Mavilia says, when he and three friends in Washington, D.C. rendezvoused for dinner at Ghibellina’s, an Italian gastropub in Logan Circle “specializing in Neapolitan-inspired pizzas and craft cocktails,” says the online restaurant guide “Popville.”
It was last November, Mark Mavilia says, when he and three friends in Washington, D.C. rendezvoused for dinner at Ghibellina’s, an Italian gastropub in Logan Circle “specializing in Neapolitan-inspired pizzas and craft cocktails,” says the online restaurant guide “Popville.”
Hold the pizza! Mavilia, who is art director at the Association of American Medical Colleges, couldn’t wait to tuck into the pasta-bolognese, his favorite dish. “In my opinion,” he says, “it’s the best in the city.”
Or rather was the best. When the foursome assembled outside the restaurant, they were disappointed to find Ghibellina’s had closed. “They had shut down for good,” Mavilia says, adding: “It was not boarded up. Just a note on the door thanking patrons for their support. I will surely miss the bolognese.”
The Ghibellina brand was later consolidated into a sister restaurant called Via in Ivy City.
Mavilia’s experience in Washington is typical of a nationwide phenomenon. Tens of thousands of restaurants and bars and eateries of every kind have closed their doors as the Covid-19 pandemic has ravaged the country and Americans have sharply limited their social interactions. As U.S. fatalities surpassed 410,000 in January, the economic damage to the restaurant and bar businesses has been staggering.
 “Washingtonian” magazine keeps a running tab of restaurants that have closed their doors in and around the nation’s capital owing to the pandemic. In December, its tally listed 75 casualties in The District alone, including such icons as the Post Pub and Montmartre, Momofuku and Tosca, plus many more in the Maryland and Northern Virginia suburbs.
“Washingtonian” magazine keeps a running tab of restaurants that have closed their doors in and around the nation’s capital owing to the pandemic. In December, its tally listed 75 casualties in The District alone, including such icons as the Post Pub and Montmartre, Momofuku and Tosca, plus many more in the Maryland and Northern Virginia suburbs.
The area around the White House dominated by the influential K Street law firms and lobbyists, and the World Bank and International Monetary Fund has been nearly barren. With few people trickling into the central city, says Madeleine Watkins, owner of 202strong, a fitness club featuring personal trainers, her business is getting battered. Receipts are off by 80% over last year and she sees the effects all around her.
“There are definitely a lot of restaurants closed, but I’m hoping and praying that lot of it is temporary,” she says. “We need people to come downtown for Washington to be a vibrant and bustling city with coffee shops, restaurants, and sandwich shops.”
One hopeful sign: Tosca, a white-tablecloth restaurant near Metro Center which boasts an enthusiastic, upscale audience and earns 4.8 stars from customer reviews, promises to re-open in the spring. “This was my go-to Italian restaurant near my office,” declares Deborah Meshulam, a partner at multinational law firm DLA Piper and a former lead trial counsel at the Securities & Exchange Commission. “I loved their grilled Branzino and pretty much anything else they made.”
The Minneapolis Star-Tribune recently counted 94 restaurants that had closed down permanently in the Twin Cities. “Saying goodbye to a beloved watering hole, a neighborhood café or a four-star restaurant is never easy,” reporter Sharyn Jackson wrote in late December. “But in 2020, the pain kept coming as the pandemic brutalized the Twin Cities hospitality industry.”
Among the notable casualties, were Bachelor Farmer, Muddy Waters, and Fig+Farro.
Angharad Bhardwaj, communications manager at medical technology company GenesisCare and a lifeling Minnesotan, told deBanked of her sorrow at learning that Fig+Farro had closed. “My husband and I were there for their opening, and I am so sad to see it close,” she says. “This was one of our favorite restaurants, just steps away from our condo in Uptown. We spent our first Valentine’s Day there. It was fresh vegan food. We even sat with the owner’s children one night. The little boy was helping his parents with the restaurant, taking orders.”
In Denver, online entertainment publication “Do303” recently highlighted closures of 15 area restaurants it called “the great ones that kept our hearts and bellies full for years.” Notable among the cohort was El Chapultepec, 12@Madison, and Biju’s Little Curry Shop. Michelle Parker, a Denverite who has a short commute to suburban Westminster where she is the City Clerk, says: “The feeling around town is that this has been a big loss to neighborhoods and to the food scene, which was just coming into its own as the pandemic hit.”
 Nationwide, more than 110,000 restaurants, bars and food-service establishments have closed their doors, reports the National Restaurant Association, the premier Washington-based trade group representing the food-service industry. The membership includes not only restaurants, pubs and cafes but non-commercial restaurant services, cafeterias, institutions like college cafeterias, and even food services at military installations.
Nationwide, more than 110,000 restaurants, bars and food-service establishments have closed their doors, reports the National Restaurant Association, the premier Washington-based trade group representing the food-service industry. The membership includes not only restaurants, pubs and cafes but non-commercial restaurant services, cafeterias, institutions like college cafeterias, and even food services at military installations.
The food-service industry is the nation’s second largest private employer and accounts for $2.1 trillion in economic activity, reports Vanessa Sink, director of media relations at the trade group. On average, when a restaurant closes, fewer than 50 people find themselves unemployed, but it adds up. As many as eight million food-service workers – waiters and bartenders, hosts and hostesses, cashiers, general managers and dishwashers, parking valets and cooks and chefs — were out of a job at the height of the pandemic in early 2020.
Curtis Dubay, senior economist at the U.S. Chamber of Commerce in Washington, D.C., notes that a whole array of food-service jobs are interwoven into the fabric of the U.S. economy. “Anything that involves large gatherings – transportation, travel and tourism, athletic events, the theater, the hospitality industry,” he says. “In places like The Hyatt in Orlando, food-service workers are involved in setting up a ballroom for conventions and small meetings. It’s a big part of the economy.”
Since the spring, many of the lost jobs came back as restaurants were able to add take-out and delivery services. Many states and localities allowed restaurants to re-open with outdoor-seating, limited occupancy, customer-spacing, and Plexiglas booths. Through the end of November, 2020, 75% of the lost jobs were recovered but 2.1 million food-service jobs had still vaporized.
As more and more people prepare their own meals at home, the switch from dining-in to curbside and takeout services has met with limited success. For take-out people are more likely to order fast-food from Chick-fil-A or Pizza Hut and Domino’s rather than something fancy. “Who wants to spend $60 for a meal you have to eat out of a cardboard container,” one Minneapolis woman complained to deBanked.

Restaurant closures, meanwhile, are having devastating consequences across a broad swath of society. “When a restaurant closes or has to cut back, it not only impacts the economy of the local community, it also affects the culture of the community,” says Sarah Crozier, communications director at Main Street Alliance, a 30,000-member, small-business advocacy group headquartered in Washington, D.C. “Local, independent places are where we create our memories as cities and towns. From losing the cries of “Keep Austin Weird” to stripping away the innovative recipes coming out of Raleigh, N.C., it deeply scars the culture and feeling of a place when we have only chain restaurants to fall back on.”
Adds Sink: “Restaurants are the cornerstone of communities. You often find that neighborhoods and local economies have built up around a restaurant. Restaurants provide jobs, they pay rent and contribute to the tax base. Other businesses will grow up around them. People will go to a restaurant – and then they’ll go next-door to shop.”
Food-service establishments are also long-term tenants. The “vast majority” of the closures, Sink asserts, have involved restaurants that had been in business for more than 16 years. Roughly one in six had been in operation for 30 years or more.
Backlit downtown restaurants with inviting awnings, valet parking and limousines idling out front are giving way to boarded-up buildings, many battened down with battleship-gray steel shutters. “I’ve been talking to mayors about empty storefronts and the effects of business failures,” says Karen Mills, former administrator at the U.S. Small Business Administration and a senior fellow at Harvard Business School, says. “It’s significant. It devastates the whole community and brings down the whole environment. People don’t want to go downtown to Main Street anymore.”
Many cities and towns have invested heavily to revitalize their inner cities and urban areas around restaurants and bars to add sparkle to the nightlife and draw visitors and tourists. The economic development strategies often commingle trendy restaurants and nightclubs, shops and boutiques with spruced up warehouses or old buildings converted into artists’ studios, lofts and apartments.
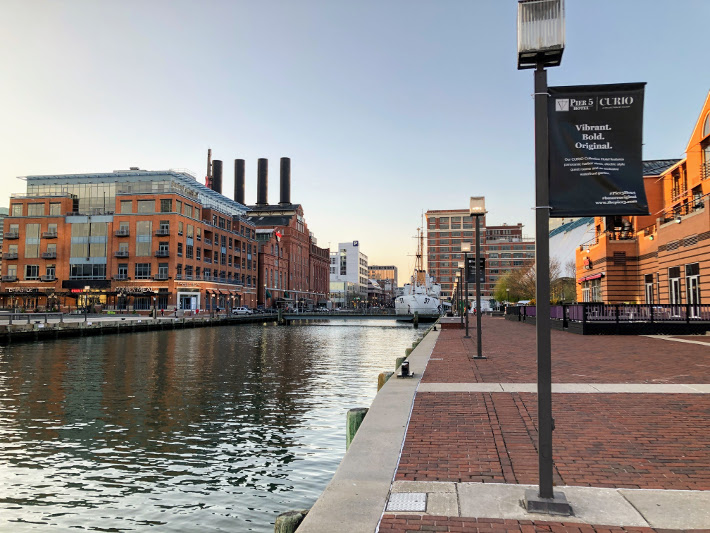 Some cities feature sports arenas and stadiums as a major draw, and the food offerings go beyond hotdogs, peanuts and Cracker Jack. St. Louis’s “Ballpark Village” promises, according to its website, a “buzzing, sports-themed district close to Busch Stadium with restaurants, bars and nightlife venues”; Baltimore’s Inner Harbor, which is walking distance to Oriole Park at Camden Yards, features a science center, aquarium and historic warships moored at the dock, as well as a complex of bars, eateries and music venues in a repurposed electric-power station known as “Power Plant Live!”
Some cities feature sports arenas and stadiums as a major draw, and the food offerings go beyond hotdogs, peanuts and Cracker Jack. St. Louis’s “Ballpark Village” promises, according to its website, a “buzzing, sports-themed district close to Busch Stadium with restaurants, bars and nightlife venues”; Baltimore’s Inner Harbor, which is walking distance to Oriole Park at Camden Yards, features a science center, aquarium and historic warships moored at the dock, as well as a complex of bars, eateries and music venues in a repurposed electric-power station known as “Power Plant Live!”
Beyond Main Street, restaurant closures are part of the collateral damage in suburbia as pandemic-wary people work and shop from home. “As I go around from town-to-town on Long Island and shoot out to the malls, I can see business closings everywhere,” says Ray Keating, chief economist at the Small Business & Entrepreneurship Council, a Washington-based trade group claiming 100,000 members. “When one business shutters, it affects other businesses. There’s a ripple effect.”
Adds Sink of the restaurant association: “Restaurants are often located with the anchor store inside malls. You never find any kind of mall without some sort of food court.”
When a restaurant closes its doors, it has a knock-on effect as well, sending shockwaves coursing up and down the supply chain. Prior to the pandemic, Sink reports, the industry generated $2.5 trillion in economic activity and supported 21 million jobs. Cutbacks in food service hurts “everything from butchers and farmers and distillers to the Cisco and Aramark food companies that depend on restaurants.
“It will reach farther back into the economy,” she adds, causing economic pain to such disparate businesses as cleaning companies, local plumbers, handymen, and maintenance workers. Even “technology companies that provide systems (for restaurants) to run a credit card or make reservations or keep track of service orders” are affected.
Andrew Volk, owner of the Portland Hunt & Alpine Club, a restaurant and bar with the reputation for offering possibly the tastiest cocktails in Maine, says that keeping his business going hasn’t been easy. The establishment was forced into lockdown in March and “stayed dark until Memorial Day,” he says, when it got the green light from the state to sell food and cocktails to go. On July 4, the restaurant went to outdoor seating, which it maintained until New Year’s Eve, adding heaters and umbrellas in the autumn to fend off Maine’s frigid temperatures.
Volk reckons that his restaurant’s sales were off by roughly 55 percent in 2020 over the previous year. Fully 95% of revenues go to pay expenses, including rent and utilities and employees’ wages. And the rest of the money scarcely lands in the cash register before it’s passed on to his vendors.
But as he has cut back operations, all of his vendors are feeling the pinch as well. There are no longer twice-weekly deliveries from the local package store from which, by state law, Volk is required to purchase hard liquor. His beer purchases –- craft beer prepared by Rising Tide Brewery and Oxbow Brewery, both of Portland, as well as Miller, Budweiser and Narraganset, the popular Rhode Island-made brew – are no longer so robust. Volk has also reduced his procurement of French and South African wines from importers.
 Purchases of farm-to-table produce from Stonecipher Farms, Dandelion Springs, and Snell Farms, which came to a halt last March, remain diminished. The daily deliveries from Baldor Specialty Foods, a New York-based food supplier of, among myriad foodstuffs, out-of-season vegetables and citrus fruit, are less frequent.
Purchases of farm-to-table produce from Stonecipher Farms, Dandelion Springs, and Snell Farms, which came to a halt last March, remain diminished. The daily deliveries from Baldor Specialty Foods, a New York-based food supplier of, among myriad foodstuffs, out-of-season vegetables and citrus fruit, are less frequent.
Volk is still offering fresh cooked fish for take-out, including cod, trout, halibut, hake and shrimp (but not cold-water Maine lobster). Even so, he’s ordering less seafood from Browne Trading Market. He has also cut back on specialty soft cheeses he buys from several local dairy farms, including Larkin’s Gorge and Fuzzy Udder.
Other vendors affected include Portland Paper Products, which supplies him with paper goods such as toilet paper and paper towels, cleaning supplies and chemicals for the dishwasher. One bright spot for the paper products supplier: it is meeting Volk’s increased demand for take-out boxes, paper napkins and plastic utensils.
Meanwhile, Volk is not looking as much to Pratt Abbott Cleaners for freshly laundered linens such as tablecloths, napkins, and kitchen shirts. Capone Griding Company in Boston, which sharpens kitchen knives and cutlery, isn’t making as many pickups and deliveries these days.
Ian Jerolmack, owner-operator of 10-acre Stonecipher Farms in Bowdoinham, Maine, is one of Volk’s food suppliers. He has been providing fresh, farm-to-table produce to several dozen restaurants in Portland, plus a couple “up the coast,” he says, since he began tilling the Maine soil a decade ago. Now the grower of organic fruit and vegetables – a garden of delights that includes tomatoes, carrots, beets, onions, cabbage, turnips, squash, sweet potatoes, and fennel – has been feeling the economic hardship along with the restaurants.
 By year-end 2020, Jerolmack says, he is down to only 15 restaurants as customers, a two-thirds attrition from his 45 customers prior to the pandemic. “Our farm was sort of unique in that it almost exclusively sold to restaurants,” he says. “They’re all in various degrees of agony,” he adds, “and I don’t know how the dust will settle. It’s been super-bizarre.”
By year-end 2020, Jerolmack says, he is down to only 15 restaurants as customers, a two-thirds attrition from his 45 customers prior to the pandemic. “Our farm was sort of unique in that it almost exclusively sold to restaurants,” he says. “They’re all in various degrees of agony,” he adds, “and I don’t know how the dust will settle. It’s been super-bizarre.”
When the restaurants went into lockdown last March, Jerolmack was faced with zero demand for his produce, and his livelihood was in jeopardy. At the same time, he was forced to reckon how much seed to plant. “There’s only one window in which to plant seeds,” he explains.
He had to decide whether to take on fulltime seasonal workers, which is not a simple proposition. In order to plant, tend and harvest his crops, he’d need to hire and house four Mexican workers under the federal government’s H-2A visa program. By law, he says, he was required to guarantee the foreign workers payment of 75% of their wages for eight months of employment. “I felt as if I were drowning,” he says. “It was a heavy weight.”
He opted to hire the H-2A workers and forged ahead with the planting, albeit at reduced acreage, consoling himself with the farmer’s ancient adage: “People always need to eat.”
With restaurants closed, his only recourse would be to sell directly to consumers. Yet Jerolmack had no online presence and was pretty much frozen out of the local farmers markets. So he turned to local restaurants and arranged to sell produce to their top customers. “I threw together a ‘farmer’s choice,’” he says, “a mixed bag of chard, carrots, onions, and beets – or whatever vegetables were in season and charged $25 a bag.”
Right away, he was able to sign up 175 customers paying $100 apiece for four weeks of produce, enough of a cushion for him to sell his “storage crops” and stay in business. Individual customers were grateful to buy the fresh organic food and avoid grocery stores, he says, the arrangement worked out for the restaurants. “They got increased foot traffic and helped their takeout business. Everybody loved it.”
By being creatively entrepreneurial and employing several direct-to-consumer sales strategies, he was able to chalk up revenues of $300,000 in 2020. That’s a hefty, 35% drop compared with the $440,000 in 2019 gross receipts. But Jerolmack says he kept five fulltime workers employed, he’s got a new consumer trade, and he’s getting ready for the 2021 planting season.
Thomas McQuillan, vice-president for strategy, culture and sustainability at wholesale food distributor Baldor, says that in a given year his Bronx-based company – with major operations centers in Boston and Washington, D.C. – delivers high-quality food to 10,000 restaurants from Portland, Me. to Richmond, Va. The wholesaler also supplies food in bulk to corporate dining rooms and cafeterias, hotels, institutions like hospitals and schools, and sports stadiums.
Baldor buys its produce from 1,000 regional farms, both big and small, and trucks in out-of-season produce from the West Coast. A visit to the company’s website discloses a vast cornucopia of edibles and victuals for sale. A few clicks discloses a gastronomic wonderland of fruits and vegetables, organics and cold cuts, meat and poultry and seafood, specialty and grocery items, dairy and cheese, bakery and pastry, and wine.
When the pandemic hit and restaurants went on lockdown, Baldor’s business plummeted by 85%, McQuillan reports, and the company reacted in much the same way as the Maine farmer. “With Covid-19,” says McQuillan, “all industries in the food business were affected. But we knew that the same number of people in our geographic area would be looking for food and we pivoted to a business-to-consumer platform and began shipping directly to people at home.
“We also knew many corporate types were no longer working in offices and, early on in the pandemic, people were fearful of going to grocery stores,” he adds, “and we began deliveries to apartment buildings all over New York. It’s not that different from delivering to a restaurant.”
According to a New York Times story, the company required a $250 minimum for consumer purchases and delivered 6,000 items within a 50-mile radius of New York City. McQuillan told deBanked it pressed its 400-truck fleet of “sprinter vans to tractor trailers” into service for the residential deliveries. The consumer business and limited restaurant re-openings allowed Baldor “to rebound, but nowhere near pre-Covid levels,” he says. By year-end 2020, the company had furloughed 20% of its workforce.
 Fresh fish is for sale on the fishmonger, outdoor seafood market.[/caption]The seafood industry was among the hardest hit by the pandemic’s throttling back the restaurant industry, says Ben Martens, executive director of the Maine Coast Fishermen’s Association. Seafood is much less likely than poultry or meat to be prepared at home or ordered for takeout. Groundfish like flaky cod, haddock, pollack, hake and flounder, he explains, are especially popular dishes in high-end restaurants in New York, Boston and Chicago.
Fresh fish is for sale on the fishmonger, outdoor seafood market.[/caption]The seafood industry was among the hardest hit by the pandemic’s throttling back the restaurant industry, says Ben Martens, executive director of the Maine Coast Fishermen’s Association. Seafood is much less likely than poultry or meat to be prepared at home or ordered for takeout. Groundfish like flaky cod, haddock, pollack, hake and flounder, he explains, are especially popular dishes in high-end restaurants in New York, Boston and Chicago.
“Seafood is a celebratory food,” Martens says. “It’s a food people embrace when things feel good. It’s covered in butter and people eat it outside when they’re with family and friends.”
Early data, he says, showed a 70% decline in “landings revenue” at the non-profit Portland Fish Exchange Auction, the major marketplace connecting fishermen with wholesalers and processors. Some fishermen and lobstermen have had some success selling directly to consumers by switching over to scallops and other seafood popular with Mainers who, Martens asserts, are somewhat more inclined to prepare seafood at home than people in other states.
But what has really given the industry a boost, he says, has been an anti-hunger program run by his trade association. Seeded with $200,000 from an anonymous donor, and bolstered with $200,000 received through the CARES Act passed by Congress last year, the program purchases seafood at a fair price and funnels it to food pantries. “Maine is the most food-insecure state in the country,” Martens says. “and high quality protein is hard for a lot of people to find.”
The program contributed enough fish portions to contribute to 180,000 meals in 2020, while helping soften economic damage to fishermen. “Now we’re seeing some stabilization with outside restaurant seating,” Martens says.
Sam Cantor, who is vice-president for sales at Gotham Seafood, a New York broker doing an estimated $16 million in sales, according to Buzzfile, sounded glum and subdued in a telephone interview with deBanked. He reports that the company delivers salmon, tuna, lobster, King Crab legs, red snapper and other seafood directly to eateries in Manhattan as well as the tri-state region of New York, Connecticut and New Jersey.
The last year has been a burden. “A ton of places are closed — cafeterias, cafes, hotels,” he says. “People are not going to the Berkshires or the Hamptons, offices are closing. In the beginning of the pandemic when (New York Governor Andrew) Cuomo shut down indoor dining it was brutal. And it’s still a difficult situation.”
Describing layoffs at the company as “significant,” Cantor says it’s also been emotionally draining to see the misfortune that has befallen restaurant workers. “It’s been a hard thing to witness,” he says. “A lot of our relationships are with chefs and they have families.”
Gotham has had some success selling directly to consumers by revamping its website and putting money into advertising on the online platforms Facebook and Instagram, he says, but “we’re not back to 100%.”
Cantor also says he is concerned that the country’s commercial infrastructure is at risk of fracturing. “It’s more than just losing your favorite restaurant or what happens to the individual fisherman and farmer,” he says. “It takes a very intricate supply chain for you to get your favorite fish. There’s a lot of work that goes into it.
“I hope my kids don’t have through something like this,” he went on. “The home delivery has been a shining light. But we want travel and tourism to come back. We want people going back to The Garden to watch the Knicks. I’m hoping there will be a renaissance, and this is just the start of the Roaring Twenties.”
Doorvest Raises $2.5M in VC Funding
January 27, 2021 San-Francisco based online real estate investment firm Doorvest announced today it received $2.5 million in VC funding with Mucker Capital leading the round.
San-Francisco based online real estate investment firm Doorvest announced today it received $2.5 million in VC funding with Mucker Capital leading the round.
Doorvest used the opportunity to announce a “Home Renovation Guarantee,” a pledge to cover all renovation-related repairs and maintenance on a new investment property for the first year.
Doorvest offers users an online platform to invest a range of $20,000 to $100,000 in rental properties. The firm handles everything from purchasing the properties to renovating, and leasing; paying the dividends back to investors.
“The true cost of hidden repairs and maintenance during the first year of homeownership often comes as a surprise as it’s difficult to predict,” CEO and Co-Founder of Doorvest Andrew Luong said. “We’ve found that the biggest mental hurdle to purchasing an investment home is the uncertainty of maintenance costs and repairs.”
 The new funding adds to the total $3.6 million the firm has raised to date, aimed toward bringing retail-investor liquidity to the estimated $3 trillion real estate market. William Hsu, the co-founder of Mucker Capital, will be joining Doorvest’s board of directors. According to the Federal Reserve, Americans who invest in real estate are on average worth 40x more than Americans with no skin in the game, Hsu said.
The new funding adds to the total $3.6 million the firm has raised to date, aimed toward bringing retail-investor liquidity to the estimated $3 trillion real estate market. William Hsu, the co-founder of Mucker Capital, will be joining Doorvest’s board of directors. According to the Federal Reserve, Americans who invest in real estate are on average worth 40x more than Americans with no skin in the game, Hsu said.
“While real estate is the #1 most favored investment asset class for Americans, only 5% of Americans own investment real estate,” Hsu said. “Doorvest’s platform has hit a nerve since launch. It has seen a 32% month-over-month increase in customers since the pandemic hit. This entirely online model naturally gains more appeal, and customers seek out safe yet easily accessible investment vehicles away from other volatile and inflationary markets.”
Newest Round of PPP Funding Faces Some New Technical Issues
January 26, 2021New technical issues are plaguing the latest round of PPP funding, according to Rob Nichols, the President and CEO of the American Bankers Association. On Monday, Nichols wrote to the acting heads of the SBA and Treasury addressing them.
Though thousands of businesses are awaiting forgiveness, the SBA’s online portal is not allowing a second loan to be processed unless pending first-round forgiveness applications are marked as complete. This runs contrary to the official SBA rules that state a borrower can apply if they can prove they spent their first loan correctly by the time they get a second.
“We urge SBA to fix this technical error and permit a lender to upload a borrower’s second draw PPP loan application irrespective of the status of the borrower’s First Draw Loan forgiveness application,” Nichols wrote. “More broadly, lenders are receiving a high number of incorrect error messages when the lender attempts to submit PPP loan applications through the portal.”
Part of those errors come from confusion Nichols writes, between previous guidance handed out by the SBA and current stipulations. Funders are unclear as to why a $30,000 per employee loan cap exists or why some borrowers found that the documentation they prepared to prove a 25% reduction of revenue met requirements two weeks ago but don’t meet the criteria recently, Nichols wrote.
Why Funders Are Investing in Real Estate As Their Side Hustle of Choice
January 25, 2021
 After five years in finance, Peter Ribeiro decided to strike out on his own and start US Business Funding in 2008, providing equipment leasing and financing for businesses. But when the housing market collapsed four months later, Ribeiro saw a second major business opportunity emerge. Earlier that year, he had purchased a $250,000 home in southern California that appraised for $355,000 at the time he bought it. Within seven months, the home’s value plummeted to $95,000. “I told myself I knew the area really well, so I might as well start buying some properties.”
After five years in finance, Peter Ribeiro decided to strike out on his own and start US Business Funding in 2008, providing equipment leasing and financing for businesses. But when the housing market collapsed four months later, Ribeiro saw a second major business opportunity emerge. Earlier that year, he had purchased a $250,000 home in southern California that appraised for $355,000 at the time he bought it. Within seven months, the home’s value plummeted to $95,000. “I told myself I knew the area really well, so I might as well start buying some properties.”
At that point, Ribeiro’s fledgling company still wasn’t generating much revenue. “I thought, ‘Man, I just can’t get a lot of loans done right now. I only have three or four employees.’ That’s how I got into the real estate industry.” Twelve years later and at the height of a global pandemic, Ribeiro is simultaneously running two thriving ventures —US Business Funding, and a portfolio of hundreds of rental properties he now owns.
At a time when fintech startups and other industry innovators are looking for investors, alternative lending execs like Ribeiro are instead choosing to put their money in real estate to beef up their investment portfolios. Although some execs shy away from talking publicly about their real estate dealings, citing the fact that they don’t want too much exposure, the consensus is that there’s a lot of money to be made in buying, selling and renting property – if you know what you’re doing.
 “I think real estate is lucrative because when you look at the history of investments, there are two or three ways to really make money: You can put your money in the stock market, or you can put it in bonds. And the other one guaranteed to go up in value is real estate,” Ribeiro says.
“I think real estate is lucrative because when you look at the history of investments, there are two or three ways to really make money: You can put your money in the stock market, or you can put it in bonds. And the other one guaranteed to go up in value is real estate,” Ribeiro says.
To Ribeiro, real estate offers a few major advantages: It’s a tangible asset. You can leverage it as it appreciates in value. Deductions make it so you pay very little in taxes. And it offers significant cash flow. “It’s the best investment you can make,” he says.
What makes real estate an especially good fit for alternative lending and fintech execs is that they possess the skills, resources and financial literacy to succeed at it.

“Real estate is a long-term gain,” Ribeiro says. “The industry we’re in is a cash-flow cow. People who are doing well are printing money. But what can you do with that money? You can put it in the stock market, but you won’t control much. Then you pay capital gains on it.”
 Attorney Paul Rianda, who represents both cash advance clients and real estate investors, says it makes sense that real estate investing appeals to alternative lenders – especially amidst the uncertainty of COVID-19.
Attorney Paul Rianda, who represents both cash advance clients and real estate investors, says it makes sense that real estate investing appeals to alternative lenders – especially amidst the uncertainty of COVID-19.
“If you’re a cash advance guy and COVID happened, then you’re not doing very well,” he says. “If you diversified your assets by doing real estate and cash advance, you’re able to weather these downturns a lot more easily than you would otherwise.”
Rianda has not yet counseled any of his own cash advance clients on real estate matters. But based on his insights from working with both areas, he says real estate would be a logical move for MCA executives, and he’s seen some of his clients in the bankcard industry buy up properties.
“One of my clients had a portfolio of merchants and sold it for a few million, then flipped over to real estate. So it’s a means (to an end),” Rianda says.
‘Snowball effect’
Ribeiro has relied on a simple strategy to steadily build his portfolio of residential properties: Buy. Fix. Leverage. Repeat.
“I feel like the portfolio is doubling every couple of years. It’s just a snowball effect,” he says.
After Ribeiro buys a home, he waits about six months before he has it appraised and fixes it up in the meantime.
“If you go to the bank within the first six months of purchasing it, they’re going to give you the actual market value of whatever you purchased the house for,” he says. “If you wait six months, they’ll reappraise the home and give its true market value, which could be another 40, 50 or 60 percent. And so now you’re going to have a lot more equity in the house, and you’re going to get a lot more money when you leverage that home to go buy the next one.”
Ribeiro says he sees lots of people making the mistake of buying a home, and then going to the bank a week or two later for a loan.
 Constantly maintaining a positive cash flow is Ribeiro’s number one rule of real estate investing. “Your best friend is depreciation,” he says.
Constantly maintaining a positive cash flow is Ribeiro’s number one rule of real estate investing. “Your best friend is depreciation,” he says.
Depreciation refers to one of the key tax benefits of real estate. Since owning a rental property is technically a type of business because it generates income, the property is considered a business asset. The IRS allows you to deduct the cost of acquiring that asset – the property – over the span of its useful life. For residential properties, the IRS sets a standard depreciation period of 27.5 years.
So if you buy a $100,000 property with a $20,000 land value, $80,000 of the asset is considered depreciable. Over the course of 27.5 years, you can take an annual deduction of just over $2,900 a year.
The trick, Ribeiro says, is to stick to lower-priced properties with an 80/20 home-to-land value. Most of his properties are single- and multifamily homes between southern California and Las Vegas.
Like Ribeiro, Rianda’s investor clients concentrate on one geographic area to find the best properties. “They look at the area for a long time, understand the area,” he says. “In my neighborhood, three blocks can make a 50 percent difference in the price of a house. You need to focus on a particular geographic area and do a lot of transactions in it.”
Small portfolio, big impact
 Real estate investing has provided a way for Jared Weitz to earn more money while being able to focus on his primary job as CEO of New York-based United Capital Source Inc., the company he founded.
Real estate investing has provided a way for Jared Weitz to earn more money while being able to focus on his primary job as CEO of New York-based United Capital Source Inc., the company he founded.
“For me, it’s just a really good second income stream and a way to have a secure return of 4.5% to 6.5% a year,” he says.
Growing up, Weitz got a feel for real estate by watching his uncles invest in multifamily properties. At one point, Weitz’s uncle owned 15 different multifamily homes, and Weitz would help do the maintenance on them.
Eight years ago, Weitz invested in his first two-family home and has fixed and flipped eight properties since then. He currently owns two two-family homes and invests primarily in multifamily homes in Long Island, Brooklyn and Queens. Over the next five years, he plans to pick up at least two more four- or eight-family properties. Working with a small portfolio of residences in his home state has allowed Weitz to have full control over managing his properties and to turn a good profit.
“I think for me, it just offers more liquidity,” he says. “It’s an asset I can sell and liquidate at any time. That’s really important for me.”
Ideally, Weitz would like for his investment to build generational wealth that he can pass down to his son. With many people in the U.S. unable to qualify for mortgages, Weitz sees real estate investing as an opportunity to help the economy by giving renters a place to live and put down roots. “Depending on the neighborhood, you can put yourself in a situation where you have good renters for 20 to 30 years. They want to raise their families and have their kids grow up there,” he says.
Litigation among the pitfalls
Even though Ribeiro has had success with his business model, he cautions that there’s considerable risk involved with real estate.
“I love the industry. It’s a passion. It’s beyond my wildest dreams of the size of the portfolio and how well it performs,” he says. “But don’t think it’s all cupcakes and unicorns. There’s a lot to the madness. That’s why not everyone can replicate the model.”
 “Professional litigators” and multiple lawsuits from renters are a major downfall that Ribeiro points to. He sees at least one substantial suit each year and tries to settle outside of court whenever possible.
“Professional litigators” and multiple lawsuits from renters are a major downfall that Ribeiro points to. He sees at least one substantial suit each year and tries to settle outside of court whenever possible.
As an attorney, Rianda says his real estate clients call on him not just for the purchase of the property, but for various issues that occur during the ownership period.
Here’s one scenario: A property owner has a tenant who isn’t paying rent, so the property owner sues the tenant. But while the lawsuit proceedings are under way, the tenant declares bankruptcy, which puts a stall on further litigation.
“There are people who understand the system and can make it difficult for you to get them out (of the property),” Rianda says, adding that it’s important to have legal counsel readily available. “You need someone who has really done this a lot and knows how the system works to get that person out of the rental property as quickly as possible.”
To minimize liability, Ribeiro has divided his properties into about 10 different business entities – each with a separate umbrella insurance policy.
Rianda sees his own real estate investor clients follow this strategy by grouping multiple homes under the name of an LLC. “If you personally own all these various assets, there’s the potential that if something catastrophic happened at one, it could bleed into all your other properties and potentially put them at risk,” he says.
Dual careers
Ribeiro’s real estate investments and finance company both serve as full-time occupations for him. Some years, he’ll focus more on one area than on the other, depending on market conditions. He spent more time on real estate between 2008 and 2013; then his business needs flip-flopped when real estate prices started going back up. This past year, he’s directed more attention to the finance company because of COVID, which necessitated some operational changes and a need to help clients who had been trying to get PPP loans. But he’s also started investing in commercial real estate, which has taken a hit because of companies forgoing office space to save overhead costs while employees work remotely.
Ribeiro expects to start seeing more mortgage defaults on lower-level homes in 2021 and 2022, after forbearance periods are over. And he’s been leveraging his assets to start buying more properties around the second quarter of the new year. “I think it will be a good time to start buying heavy again,” he says.
An attractive investment vehicle
With the pandemic weakening business portfolios, secondary investment options might sound like just what the doctor ordered.
 When COVID first hit, some of Rianda’s clients started pursuing other investments like personal protective equipment (PPE). Most of his cash advance clients closed up shop for a few months.
When COVID first hit, some of Rianda’s clients started pursuing other investments like personal protective equipment (PPE). Most of his cash advance clients closed up shop for a few months.
“As time goes on, I’m starting to see my clients go back into their lending,” Rianda says.
Even as clients start to recoup their business, Rianda sees the wisdom in other investments and says cash advance executives are well suited for real estate. “It’s just a way that people who have been successful and spin off a lot of cash for their businesses see as a safe way to diversify their income,” Rianda says. “It’s something I find that people who are doing well in their business do, regardless of what business they’re in. So cash advance guys are just following the things people have done for years.”
Ribeiro cautions that people who get into real estate should look at it as a 10-year investment minimum, and not just a two- or three-month stint.
“It’s not a lottery ticket, and it’s not an overnight race,” Ribeiro says. “This is a long-term gain. But it’s a very lucrative gain from a cash-flow perspective and a tax perspective. I don’t think there’s a more attractive vehicle than real estate.”