Archive for 2017
Nulook Capital Has Filed Chapter 11
April 13, 2017NY-based merchant cash advance funding company Nulook Capital filed for Chapter 11 on April 4th, according to court records. They listed more than $2.6 million in creditor claims. The largest among them was a secured claim for $2 million by a specialty finance company.
Two other creditors in the bankruptcy proceeding are also involved in the merchant cash advance industry.
The voluntary petition was filed in the Eastern District of New York in the United States Bankruptcy Court.
81% of Online Business Lending Borrowers Report Being Satisfied or Neutral
April 12, 2017The latest Small Business Credit Survey published by the Federal Reserve shows that 81% of small business borrowers were either satisfied or neutral about their online loan experience. Online lenders were defined as nonbank alternative and marketplace lenders, including Lending Club, OnDeck, CAN Capital, and PayPal Working Capital.
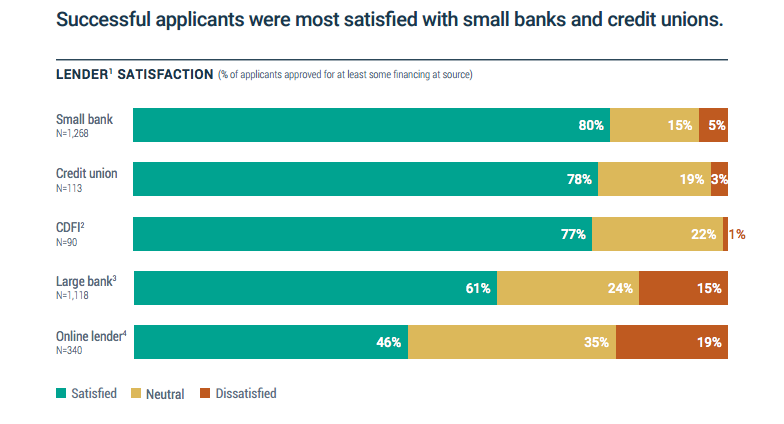
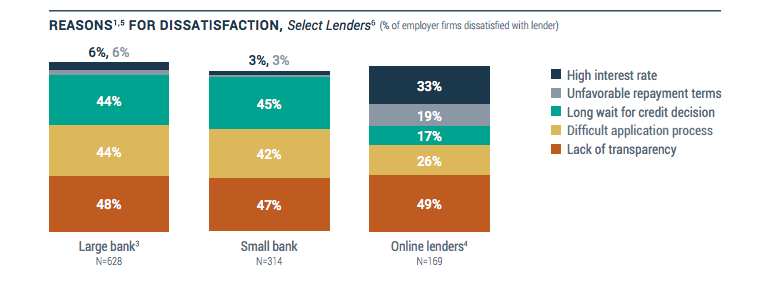
Of the 19% that were dissatisfied, nearly half cited transparency as a root cause. But that’s to be expected given that businesses dissatisfied with their loan from a large or small bank also cited transparency just as often.
While these charts indicate that there is still room for online lenders to improve, the 2016 report paints a more honest narrative than last year. Last year’s report used net satisfaction scores, which measured the difference between satisfied and dissatisfied borrowers. That methodology resulted in 15% net satisfaction for online lenders in 2015, which unless you read the fine print, easily misled even the most sophisticated of readers to conclude that only 15% of borrowers were satisfied. (Those readers included experts testifying in congressional hearings, the media, and government agencies, all of whom relied on that report to argue that online borrowers were terribly dissatisfied).
The 2016 report shows that businesses borrowing from an online lender were only slightly more likely to be dissatisfied than those that borrowed from a large bank (19% vs. 15%). And it’s the high interest rates that stand out to those dissatisfied online borrowers. 33% said that a high interest rate was the reason for their dissatisfaction. This is to be expected since non-banks inherently suffer from a higher cost of capital than banks.
Cash Advances?
Unfortunately, all of their data on “cash advances” is tainted. If they meant “merchant cash advances” or sales of future receivables, they should’ve specified such in the survey that went out to small businesses. Instead, the survey repeatedly asked about cash advances, a term most commonly associated with borrowing money through an ATM with a credit card. Those surveyed were also asked if they used personal loans, auto loans or mortgages so the multiple choice context suggests a credit card cash advance. Similarly, a cash advance could also mean a payday loan. With so many interpretations, the consequence is that it’s impossible to tell what the Federal Reserve meant or what those being surveyed thought they were being asked.
Notably, one question asked businesses if “portions of future sales” were used as collateral for a debt, but since merchant cash advances do not collateralize future sales (the future sales are actually sold, they don’t serve as collateral for a loan), it’s difficult to understand what they meant or how a respondent might interpret that.
Statistically representative?
The 2016 report also spends more time defending the Fed’s sampling methodology. Perhaps they are aware that their data is being put under the microscope.
Read the full Fed report here
Sneak Peek at the Mar/Apr 2017 Issue of deBanked
April 11, 2017 In the March/April 2017 issue of deBanked magazine, we delve into the industry’s latest trend, the push back towards traditional banking. The featured story is titled accordingly as “Re-Banked” and our many sources lay out a compelling narrative. Our cover, a sketch of a young tech CEO shedding the hoodie to reveal the suit-and-tie attire of a banker underneath, was one of several pieces of art we commissioned for this issue.
In the March/April 2017 issue of deBanked magazine, we delve into the industry’s latest trend, the push back towards traditional banking. The featured story is titled accordingly as “Re-Banked” and our many sources lay out a compelling narrative. Our cover, a sketch of a young tech CEO shedding the hoodie to reveal the suit-and-tie attire of a banker underneath, was one of several pieces of art we commissioned for this issue.
And for you brokers out there, we’ve got something really special, the inside scoop on the latest way that reps are winning deals. Today’s broker is hanging up the phone and texting merchants instead and the merchants are responding in kind. Phone calls and emails are going the way of the fax machine when it comes to gathering documents and pitching offers. The lesson we learned from the several people we interviewed is that when merchants want to know what’s next, send a text.
There’s more of course, so if you haven’t already subscribed to our free print magazine, make sure you do so here. This issue has already printed and shipped so you’ll be getting it very soon.
We hope you enjoy it!
Subscribe FREE
For Factoring, Different Spin, Same Issues as MCA
April 10, 2017
They called it the 2017 Factoring Conference, but an MCA professional would’ve hardly noticed. On the agenda was news about Dodd-Frank’s Section 1071, the now-dead NY lending legislation, usury litigation, confessions of judgment, stacking, fintech and gripes about brokers. And yet factors and MCA companies still largely live separate lives.
The underlying differences between the two industries are as much cultural as they are contractual. The International Factoring Association’s directory reports having nearly twice as many members from Texas as they do from New York. They also list having more members from Utah than they do New Jersey. Compare that to our own readership at deBanked in which website visitors and magazine subscribers are most heavily concentrated in New York, California, Florida and New Jersey. Texas ranks 8th for subscribers and Utah is much, much farther down. And while purely based on my unscientific observation, I’d wager a bet that the average age of a factoring company owner is at least a decade older (probably much more) than the average age of an MCA company owner.
Differing philosophies between the two industries are perhaps exacerbated by this generational and demographic gap.
On a fintech disruption panel at the factoring conference last week, Pearl Capital CEO Sol Lax told attendees that the MCA industry was not only innovative but ultra competitive. “You either need to evolve or become a phone booth,” he said. Other panelists explained that today’s average small business is focused on speed and simplicity and that they’ve built their models around that.
But factoring has survived the test of time. In the latest issue of The Commercial Factor, Jeremy B. Tatge traces the first factoring agreement in America to 1628. “This spirit has endured and survived wars of independence, such as the American Revolution, two World Wars in the Twentieth Century, and even down to the present day (NATO being but one of many examples),” he writes.
Will technology finally break that spirit or will today’s stereotypical young MCA company owner from New York and Florida eventually find themselves becoming older, wiser, and ready to lay down roots in the midwest? Will they trade the Las Vegas conferences for honky tonks in Cowtown?
I don’t believe that such a transition even has to happen. Whatever differences the two industries have, they are united by common causes and issues and can evolve together.
Can Factors and MCA Companies Get Along?
April 7, 2017 At the factoring conference in Fort Worth, TX on Thursday, the 2 PM panel was officially called The Fintech Disruption. But it could’ve just as easily been named The MCA Disruption considering that the panelists all ran companies engaged in either unsecured business lending or MCA. The tension in the packed room was palpable. For some factors, the competitive pressure they feel with unsecured finance companies cuts deep, down to their soul. So naturally it only made sense, being that it’s Texas and all, that they lassoed a few of those unsecured guys up and put them on stage to explain theirselves.
At the factoring conference in Fort Worth, TX on Thursday, the 2 PM panel was officially called The Fintech Disruption. But it could’ve just as easily been named The MCA Disruption considering that the panelists all ran companies engaged in either unsecured business lending or MCA. The tension in the packed room was palpable. For some factors, the competitive pressure they feel with unsecured finance companies cuts deep, down to their soul. So naturally it only made sense, being that it’s Texas and all, that they lassoed a few of those unsecured guys up and put them on stage to explain theirselves.
So what’s the best way for an MCA company to make a peace offering to a room full of factors?
Sol Lax, the CEO of Pearl Capital Business Funding LLC, kicked it off by telling the audience that a small business customer might begin their quest for capital by searching the internet for a small business loan. “There’s no factoring companies that are going to pop up,” he exclaimed, suggesting that they were already losing when it came to the Internet to acquire customers and had little hope of catching up. But if you are a small factor, he conceded, you should continue generating leads through relationship building since the Internet is now so cost-prohibitive.
Dean Landis, the President of Entrepreneur Growth Capital, ran with that and asked attendees to raise their hands if they really pay attention to the cost of lead acquisition. While this was an informal survey, virtually no one raised their hand, seeming to confirm that deal flow for factors is largely acquired through relationships. Landis, who played the role of moderator and devil’s advocate, asked if MCAs and factors were really even targeting the same customers. Would you lend to someone who already has a senior lien? he asked. “These [MCA] guys figured out how to do that.”
Dan Smith, President of Fora Financial and Paul Rosen, Chief Sales Officer of OnDeck, explained that their customers often seek a fast-paced application-to-funding process, which drew a rebuke from an audience member who had a hard time believing that so many merchants truly needed that speed and simplicity. Smith and Rosen countered by saying that customers will choose whatever is best for them and that not every customer fits their boxes.
Lax advised factors to look at the bigger picture, that one big lender on their own might not seem like a threat but that a company like OnDeck could license out their scoring model to banks and banks could adapt that to make loans to companies they have otherwise been ignoring (the same ones that go to factors) and compete against the factors directly.

As the audience chipped away with questions about the soundness of these scoring models and fintech, Smith of Fora reminded everyone that they still have underwriters that are manually overseeing deals, rather than let computers do everything entirely on their own. “You can literally fintech yourself out of the business,” Smith cautioned lenders who might overzealously replace their core competency with algorithms that don’t perform as well.
But even then, do these scoring models work when merchants gets stacked on? This question was asked and it suggests that stacked merchants have a higher risk of default. Rosen of OnDeck confirmed that when he said “customers that stack on us have much higher loss rates.” Meanwhile, Smith said that when customers are doing something that affects their model, they just need to improve their model, just like they would if there was a recession or some other economic event underway. “All of our models are built on lifetime value,” he said. They want to grow and nurture their clients, he explained.
While factors fear that MCA companies could stack on their clients, there are signs that a path forward exists. An informal poll of the room indicated that not only are factors referring prospects to MCA companies but that MCA companies are returning the favor and sending prospects to them. The former was more prevalent.
Lax of Pearl, was more pointed about the future for factors. “You either need to evolve or become a phone booth,” he proclaimed. He prefaced that with a story about a child who was absolutely befuddled by an old Superman movie, as in ‘what were all these ridiculous random booths doing in the city that enabled Clark Kent to go around changing his clothes?’ The concept of a phone booth could hardly even be explained to the next generation. “Your industry is suffering a phone booth moment,” Lax said to the factors.
Is he right?
To the unsecured lenders and MCA companies who attend the factoring conference, they invariably see value in partnerships. And for the factors still hesitant to take that step, is it really the MCA model that’s causing friction? Or is it the evolution of the way that businesses interact with financial technology, i.e. fintech? And might fintech disrupt everyone in the end?
Only time will tell.
Quotes and paraphrases were derived from the panel. The summary is my own analysis of it and much of the 90-minute discussion was omitted here for brevity.
Lending Club to Beta Hardship Plans for Borrowers (and Protect Returns for Investors)
April 5, 2017Lending Club wants to make it easier to accommodate borrowers facing hardship and in the process potentially protect the investor from unnecessary losses. A full explanation of the program was sent out to Lending Club investors on Wednesday, the full text of which we’ve pasted below:
At Lending Club, we are committed to improving experiences for both borrowers and investors. We’re excited to announce that after a beta test, we will begin offering hardship plans to borrowers effective May 4, 2017. Hardship plans allow borrowers to temporarily make interest-only payments to accommodate an unexpected life event. As part of this change we are also making additional data fields related to these plans available for investors.
Lending Club continuously looks to put lending industry best practices to work. Hardship plans are commonly offered to borrowers in the lending industry because they allow borrowers time to adjust to a life event (like a medical emergency, temporary job loss, unexpected car or home repairs, death in the family, or other events). Hardship plans are in accordance with commercially reasonable efforts to service and collect on loans, as well as with our prospectus, which provides us flexibility to work with a borrower to structure a new payment plan if needed.
Our hardship plan program specifically targets borrowers who are more likely to return to repaying their loan. Under the plan, borrowers are allowed to temporarily make interest-only payments for a period of 3 months to accommodate an unexpected life event. After 3 months, regular payment terms and obligations resume. Only borrowers who fulfill specific characteristics (such as a demonstrated history of repayment) and who claim a hardship will be offered plans. Importantly, borrowers’ loans must be either current or between 1 and 30 days past due to qualify for a hardship plan.
We believe the hardship program will work to protect investor returns as borrowers whose loans may otherwise progress to charge-off status have the opportunity to make interim payments and some portion may revert to current status.
Finally, we are adding 15 new data attributes of borrowers who utilize hardship plans to investor reports and the API. The fields will only apply for hardship plans offered as of May 4, 2017 and going forward. You can find more information on these new data fields here.
Offering hardship plans is both consistent with our values – doing the right thing by borrowers while they’re getting back on their feet – and helps to protect investor returns. We will potentially look to expand to different types of hardship plans in the future as we gain further insight into borrower behavior and continue to listen to customer feedback.
Please feel free to reach out with any questions – we welcome your feedback.
Best regards,
The Lending Club Team
Lights Out for New York’s Attempt to Impose Stricter Lending Rules
April 5, 2017 In a late night session on Tuesday, and days past the budget deadline, the New York State Senate voted 58-2 in favor of a key budget bill. Noticeably gone from it was Part EE, which would’ve imposed stricter licensing requirements on not only just lending, but also other forms of finance. Part EE was originally put there by the Governor’s office as an amendment to Section 340 of the State’s banking law.
In a late night session on Tuesday, and days past the budget deadline, the New York State Senate voted 58-2 in favor of a key budget bill. Noticeably gone from it was Part EE, which would’ve imposed stricter licensing requirements on not only just lending, but also other forms of finance. Part EE was originally put there by the Governor’s office as an amendment to Section 340 of the State’s banking law.
Over the last two months, several trade groups used what little time they had to express concerns over the language. Their biggest frustration was that no one had consulted with them in advance. In February, Dan Gans, the executive director of the Commercial Finance Coalition (CFC) said, “They should allow all the stakeholders to have their voices heard.” The CFC, which represents many small business financing companies, did their best to do just that last month by actually making the trek to Albany.
Ultimately, the legislature did not support the Governor’s plan. Both the Senate and the Assembly removed Part EE from their versions of the budget and on Tuesday night, the Senate passed it. The Assembly passed it the day after.
This is the first time the budget deadline has been missed under Governor Andrew Cuomo. The last miss was in 2010 under Governor Paterson, which came in 125 days late.
Did UCC Lead Generators Overload NY State’s System?
April 4, 2017 In the small business finance industry, New York State is known as one of the friendliest places to conduct a UCC search. You can not only search by debtor, but also by secured party, and get just about everything you need to create a list of prospects for free.
In the small business finance industry, New York State is known as one of the friendliest places to conduct a UCC search. You can not only search by debtor, but also by secured party, and get just about everything you need to create a list of prospects for free.
But the State’s website isn’t exactly a pillar of technological achievement. Indeed, the UCC Lien Search welcome page makes clear that searchers will need to be using Netscape Navigator 4.0 or higher and that version 3.0 of Internet Explorer or lower is not supported. Those browser iterations were released in 1997 and 1996 respectively, before some in the business finance industry were even born.


And the online system built for Windows 3.1 users didn’t seem to be doing so well over the last few months. Routine manual searches that I occasionally conduct were leading to error messages and crash pages instead of results. Were UCC lead generators querying the system to death?
Last week, New York took the entire UCC system down for “maintenance” and when it finally came back up, a tool to combat automated queries had been installed.
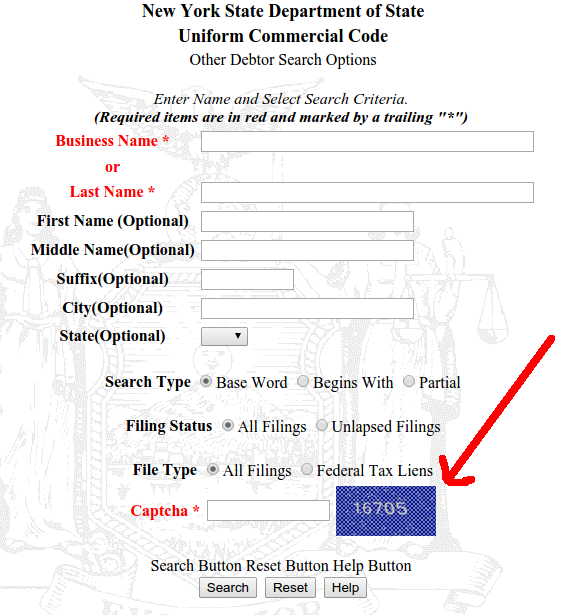
Curiously, this has only been implemented for secured party searches and other debtor search options. Standard debtor search options remains unchanged.
As Captchas are designed to thwart automated queries, could this be a sign that lead generators were crashing the system?
To check it out yourself, it’s best to be using Windows 95 or higher. Typewriters and Etch-A-Sketch users may experience performance issues.