So God Made a Farmer, But Who’s Financing The Farms?
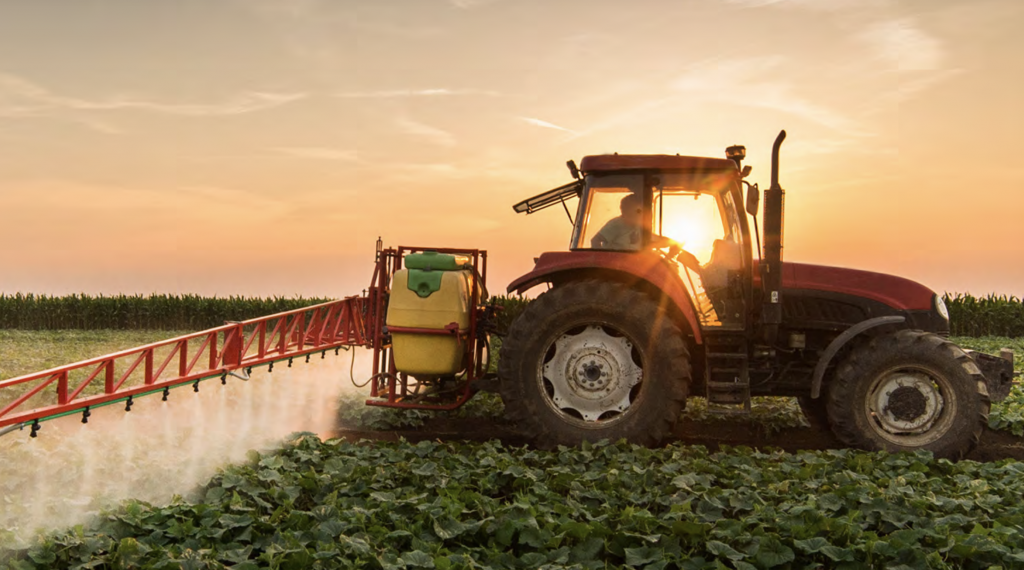 Most mornings, farmers and ranchers wake up worrying about uncooperative weather and volatile commodity prices. Just the same, they pull themselves out of bed to spend the morning tinkering with crotchety machinery or wrangling uncooperative livestock. When they break for lunch, the kitchen radio alerts them to trade wars with distant countries and the unintended results of federal regulation. As they make their way back outdoors for the afternoon’s work, they can’t help but notice another new house taking shape in the distance as suburban sprawl encroaches on the fields and pastures. By evening, their thoughts have turned to their need for short-term capital and how the local banker seems increasingly wary of providing funds.
Most mornings, farmers and ranchers wake up worrying about uncooperative weather and volatile commodity prices. Just the same, they pull themselves out of bed to spend the morning tinkering with crotchety machinery or wrangling uncooperative livestock. When they break for lunch, the kitchen radio alerts them to trade wars with distant countries and the unintended results of federal regulation. As they make their way back outdoors for the afternoon’s work, they can’t help but notice another new house taking shape in the distance as suburban sprawl encroaches on the fields and pastures. By evening, their thoughts have turned to their need for short-term capital and how the local banker seems increasingly wary of providing funds.
It’s that last challenge where the alternative small-business funding industry might be able to help, says Peter Martin, a principal at K-Coe Isom, an accounting and consulting firm focused on the ag industry. “If you as a farmer need operating funds and you can’t get them from a bank, you don’t have a lot of options,” he says. “Historically, nobody outside of banks has had much interest in lending operating money to a farmer.”
The result of that reluctance to provide funding? “I can’t tell you the number of calls I get to say, ‘Hey, I need $100,000 and I need it in a couple of days because of X, Y, Z that’s come up,’” says Martin. “We don’t have a place that we can send those people to. You could make a lot of quick turnaround loans in rural America.” What’s more, it’s a potential clientele that makes a lot of money and prides itself on paying back what they owe.
Martin’s not alone in that assessment. While farmers enjoy abundant long-term credit to buy big-ticket assets, such as land and heavy machinery, they’re struggling to find sources of short-term credit for operating expenses like labor, repairs, fuel, seed, feed, fertilizer, herbicides and pesticides, notes Mike Gunderson, Purdue University professor of agricultural economics.
 But remember that nobody’s saying it would be easy for alt funders to break into the agricultural sector. City folks accustomed to the fast-paced rhythms of New York or San Diego would have to learn a whole new seasonal business cycle. Grain farmers, for example, plant corn and soybeans in April, harvest their crops September or October, and may not sell the grain until the following January, says Nick Stokes, managing director of Conterra Asset Management, an alternative-funding company that places and services rural real estate loans.
But remember that nobody’s saying it would be easy for alt funders to break into the agricultural sector. City folks accustomed to the fast-paced rhythms of New York or San Diego would have to learn a whole new seasonal business cycle. Grain farmers, for example, plant corn and soybeans in April, harvest their crops September or October, and may not sell the grain until the following January, says Nick Stokes, managing director of Conterra Asset Management, an alternative-funding company that places and services rural real estate loans.
That seasonality results in revenue droughts punctuated by floods of revenue – a circumstance far-removed from the more-consistent credit card receipt split that launched the alternative small-business funding industry. Alternative funders seeking customers with consistent monthly cash flow won’t find them in the agricultural sector, Stokes cautions.
And while the unfamiliarity of farm life might begin with wild swings in cash flow, it doesn’t end there. Operating in the agricultural sector would require urbanites to learn the somewhat alien culture of The Heartland – a way of life based on hard physical labor, the fickle whims of the weather, and friendly unhurried conversations, even with strangers.
Even so, the task of mastering the agricultural funding market isn’t hopeless, and help’s available. Experts in agricultural economics profess a willingness to help outsiders learn what they need to know to get involved. “Selfishly, the first place I’d love to have them reach out to is me,” Martin says of alternative funders. “I’ve been writing and thinking for years about the importance of getting some non-traditional lenders into agriculture.” He would have “no qualms” about featuring specific prospective funders in a column he writes for one of the nation’s largest farm publications.
 It also requires meet-and-greets. During the winter, when farmers aren’t in the fields, funders could make connections at trade shows, Martin advises. “Word would get around rural America really quick,” he predicts. Networking with advisers such as crop insurance agents, agronomists and ag CPS’s – all of whom deal with farmers daily – would also help funders find their way in agriculture, he contends.
It also requires meet-and-greets. During the winter, when farmers aren’t in the fields, funders could make connections at trade shows, Martin advises. “Word would get around rural America really quick,” he predicts. Networking with advisers such as crop insurance agents, agronomists and ag CPS’s – all of whom deal with farmers daily – would also help funders find their way in agriculture, he contends.
Investors who are curious about extending credit in the agricultural sector could rely upon Conterra to help them locate customers and help them service the loans, says Stokes. He can even help acclimate them to the world of agriculture. “If they’re interested in investing in agricultural assets – whether that be equipment, real estate or providing operating capital – we would enjoy the opportunity to visit with them,” he says.
GETTING STARTED
Alt funders could begin their introduction to the agrarian lifestyle by taking to heart a quotation attributed to President John F. Kennedy: “The farmer is the only man in our economy who buys everything at retail, sells everything at wholesale and pays the freight both ways.”
“Agriculture is a very different animal,” Martin notes. He sometimes presents a slide show to compare the difference between a typical farm and a typical manufacturer of the same size. At the factory, revenue ratchets up a bit each year and margins remain about the same over time. On the farm, revenue and margins both fluctuate wildly in huge peaks and valleys from one year to the next.
The volatility makes it difficult to manage the risk of lending, Martin admits, while noting that agriculturally oriented banks still have higher returns than non-ag banks, according to FDIC records. “You have to go back to 2006 to find a time when ag banks didn’t outperform their peers on return on assets,” he says. “What this tells us is that, generally speaking, ag borrowers are better at repaying their loans,” he asserts. Charge-offs and delinquencies in ag portfolios are lower than in other industries, he says.
Many of the nation’s farms have remained in the same family for more than a century – a stretch of time that’s seldom seen in just about any other type of business. Besides making potential creditors comfortable that a particular operation will stay in business, the longevity of farms provides lots of documents to examine – not just tax records but also production history that’s tracked by government agencies. A particular farmer’s crop yields, for example, can be compared with county averages to calculate how good the borrower is at farming.
Debt to asset ratio on the nation’s farms stands at about 14 percent, which Martin views as “insanely low.” But that’s not the case on every farm. Highly leveraged farms have ratios of 60 percent or even 80 percent when farmers have grown their businesses quickly or encountered debt to buy land from their parents, he says. Commodity prices are low now, but farms with 14 percent debt to asset ratios still don’t have a problem, even in hard times. Farmers deeply in debt, however, have little ability to climb out of the hole. The latter are using operating capital to fund losses.
 Farmers with debt to asset ratios of 10 percent have little trouble finding credit and aren’t going to pay anything other than bank rates, Martin says. The target audience for non-traditional funding are farmers who are having trouble but will be fine when commodity prices rebound. Another potential client for alternative finance would be farmers who are quickly increasing the size of their operations when opportunities arise to acquire land. Both groups need funders willing to contemplate the future instead of demanding a perfect track record, he maintains.
Farmers with debt to asset ratios of 10 percent have little trouble finding credit and aren’t going to pay anything other than bank rates, Martin says. The target audience for non-traditional funding are farmers who are having trouble but will be fine when commodity prices rebound. Another potential client for alternative finance would be farmers who are quickly increasing the size of their operations when opportunities arise to acquire land. Both groups need funders willing to contemplate the future instead of demanding a perfect track record, he maintains.
Farmers generally need loans for operating capital for about 18 months, according to Martin. “Let’s say I borrow that money, get my crop in the ground, harvest that and I may not sell my grain right after harvest,” he says. The whole cycle can easily take 18 months, he says. Shorter-term bridge lending opportunities also arise in situations like needing a little extra cash quickly at harvest time. Farmers usually have something to put up as collateral – like producing 50 titles to vehicles or offering up some real estate, he says.
An unsecured loan – even one with high double-digit interest – could succeed in agriculture because no one is offering that type of funding, Martin says. Small and medium-sized farms would probably benefit from funding of $100,000 or less, while larger farms might sign up for that amount but often require more, he notes.
LAY OF THE LAND
The Farm Credit System, a nationwide quasi-governmental network of borrower-owned lending institutions, provides more than a third of the credit granted in rural America. That comes to more than $304 billion annually in loans, leases and related services to farmers, ranchers, rural homeowners, aquatic producers, timber harvesters, agribusinesses, and agricultural and rural utility cooperatives, according to published reports.
Congress established the Farm Credit System in 1916, and the Farm Credit Administration was established in 1933 to provide regulatory oversight. “All they’re doing is lending money to agriculture,” says Martin.
However, the system can go astray in the eyes of some observers. An arm of the Farm Credit System called CoBank lends to co-operatives and other rural entities. At one point Verizon Wireless became a borrower from CoBank, which angered some observers because the system was supposed to be helping rural America, not corporate America, Martin says.
That anger arises partly because the federal government doesn’t require Farm Credit to pay income tax, which enables it to lend at lower rates, Martin says. “Part of the allure of borrowing from Farm Credit is you can typically borrow cheaper,” he notes. “You’d be very hard pressed to find a farmer who over the years hasn’t had some interaction with Farm Credit.”
Observers sometimes fault the system for what they perceive as a tendency to extend credit only to those who don’t really need it, notes Purdue’s Gunderson. People working for the system believe they’re doing a good job of supporting agriculture, he says, noting that the system is charged with the responsibility of helping new and young farmers.
Another entity, the Federal Agricultural Mortgage Corp., also known as Famer Mac, works with lending institutions to provide credit to the agricultural sector. It’s a publicly traded company that serves as a secondary market in agricultural loans, including mortgages. It purchases loans and sells instruments backed by those loans and was chartered in 1988. Conterra, the alternative-funding company mentioned earlier in this article, -works with Farmer Mac and financial institutions to make real estate loans to farmers and ranchers in financial distress. The loans are designed to help borrowers get back on their feet in three to five years so that they would then qualify for regular bank loans.
Then there are the ag lending divisions at the large banks such as Wells Fargo, Chase and the Bank of the West, Martin says. “Lots of these big national banks are doing at least some ag lending,” he says. “Some, obviously, have bigger ag portfolios than others.”
Some regional banks focus on agriculture, Martin continues. “When you get into the middle of the corn belt, there are going to be some regional banks where traditional ag lending’s a huge part of what they do,” he says. Local banks in small towns get involved, too. “Most small community banks are going to have some kind of ag lending portfolio,” Martin notes. Hometown bankers can provide operating capital to some farmers, but only to those who haven’t experienced recent hiccups in revenue or expenses.
THE NON-BANKS
 “Then you get into the non-bank lenders,” Martin observes. “A really good example of this is John Deere,” the tractor and equipment manufacturer. The company provides a tremendous amount of capital to rural America through equipment lending and also through other credit facilities, he says. In fact some observers estimate that John Deere is the largest lender to agriculture. Even so, the company usually doesn’t provide enough non-equipment credit to become the only lender a farmer would use, he says.
“Then you get into the non-bank lenders,” Martin observes. “A really good example of this is John Deere,” the tractor and equipment manufacturer. The company provides a tremendous amount of capital to rural America through equipment lending and also through other credit facilities, he says. In fact some observers estimate that John Deere is the largest lender to agriculture. Even so, the company usually doesn’t provide enough non-equipment credit to become the only lender a farmer would use, he says.
The same holds true with other lenders to agriculture, Martin says. Co-operatives, for example, lend money to agriculture even though they’re not banks. Typically, they begin by extending credit for products like seed, fertilizer or pesticides and then start making additional credit available to farms and ranches. In recent years, a large co-operative called CHS loaned hundreds of millions of dollars in addition to selling products on credit. Some large CHS loans went bad caused a ripple effect throughout the cooperative structure, Martin maintains. Other co-ops have looked at CHS and wondered if they’re moving too far outside their core competency. So now many co-ops are tying funding to products they’re selling.
Some other non-bank lenders have shown up in agriculture, and they fall into two categories, Martin says. One group is making real estate loans in agriculture, so their loan programs are geared to farmers looking to buy land or anything that can be secured by land. Conterra and Ag America are examples. Farmer Mac lends a lot of money against farmland, as well. So farmers who have agricultural land have a lot of access to capital and a lot of lenders who want to provide it, he says.
The second group of non-bank lenders is providing operating capital. “That is a very, very small club,” Martin says. “There’s really not anybody doing this on a regular basis – with just one or two exceptions.” Probably the biggest name among the exceptions is Ag Resource Management, usually known as ARM, he continues. ARM places a value on the potential productivity of a famer’s land. Then it looks at the crop insurance the farmer’s able to buy to protect the investment in that crop. ARM then lends part of the value of that crop insurance.
Let’s say a farmer can grow $10 million worth of crops, according to ARM’s projection,” Martin says. “You can get crop insurance to cover 80 percent,” he continues. “For a total crop failure, you will get $8 million for that crop.” Using a formula based on type of crop, location and type of crop insurance, ARM will lend some amount less than $8 million. “Their collateral is pretty rock solid,” Martin observes.
ARM uses a system to make sure farmers use the funds only for expenses related to growing the crop they’re using as collateral. “Their risk of not getting a crop in the ground that qualifies for the insurance is next to nothing,” Martin says. ARM offers differing interest rates, depending upon risk, in at least the high single digits or double digits, and they also charge fees. “So you’re going to be paying a lot, but they are the lender of last resort in agriculture right now,” he says, adding that ARM operates multiple offices has grown quickly.
Through lenders like ARM, the agricultural sector’s becoming familiar with alternative finance. But much remains to be done if alt fin pioneers want to venture into the sector. Those who do will encounter a complicated credit landscape, but one that offers opportunities for anyone willing to learn about unfamiliar business cycles and lifestyles.
Last modified: May 1, 2019